Obesity Linked to Poor Brain Health in Children
Released: November 28, 2022
At A Glance
- Higher weight and body mass index are associated with poor brain health in children.
- Researchers observed structural brain changes in overweight children between the ages of 9 and 10, including significant impairment to the integrity of the white matter.
- Increased weight was associated with decreased connectivity in the functional networks of the brain that involve cognitive control, motivation and reward-based decision making.
- RSNA Media Relations
1-630-590-7762
media@rsna.org - Linda Brooks
1-630-590-7738
lbrooks@rsna.org - Imani Harris
1-630-481-1009
iharris@rsna.org
CHICAGO — Using MRI data from the largest long-term study of brain development and child health in the United States, researchers have found that higher weight and body mass index (BMI) in pre-adolescence are associated with poor brain health. The findings are being presented today at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
“We know being obese as an adult is associated with poor brain health,” said researcher Simone Kaltenhauser, a post-graduate research fellow in radiology and biomedical imaging at the Yale School of Medicine in New Haven, Connecticut. “However, previous studies on children have often focused on small, specific study populations or single aspects of brain health.”
Childhood obesity is a growing concern in the U.S. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, approximately one in every five American children is obese.
Kaltenhauser’s study used imaging data from the Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development (ABCD) study that included 11,878 children aged 9-10 years from 21 centers across the country to represent the sociodemographic diversity in the U.S.
“This dataset is unique in that it closely approximates the U.S. population,” Kaltenhauser said.
After excluding children with eating disorders, neurodevelopmental and psychiatric diseases, and traumatic brain injury, the study group included 5,169 children (51.9% female). According to the children’s BMI z- scores—measures of relative weight adjusted for a child’s age, sex and height—the overweight and obesity rates within the study group were 21% and 17.6%, respectively.
To gain a comprehensive view of brain health within the study group, the team evaluated information from structural MRI and resting-state functional MRI (fMRI), which enables researchers to measure brain activity by detecting changes in blood flow. With resting state fMRI, the connectivity between neural regions—known as resting state networks—can be observed while the brain is at rest. The researchers also evaluated data from diffusion tensor imaging—a technique that helps assess white matter—and restriction spectrum imaging, an advanced diffusion MRI technique.
After correcting for age, sex, race-ethnicity, handedness and socioeconomic status, the research team used linear models to determine associations between weight and BMI z-scores and the imaging metrics.
The researchers observed structural brain changes in children with higher weight and BMI z-scores, including significant impairment to the integrity of the white matter. Areas of degradation included the white matter of the corpus callosum, the principal connector between the brain’s two hemispheres, and tracts within the hemispheres that connect the lobes of the brain.
“It is striking that these changes were visible early on during childhood,” Kaltenhauser said.
The researchers also observed a thinning of the outermost layer of the brain, or the cortex, which has been associated with impaired executive function.
“We expected the decrease in cortical thickness among the higher weight and BMI z-score children, as this was found previously in smaller subsamples of the ABCD study,” Kaltenhauser said. “However, we were surprised by the extent of white matter impairment.”
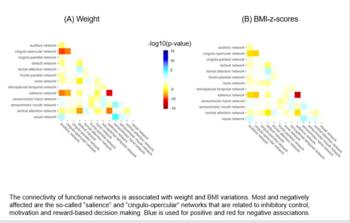
Resting-state fMRI images revealed that increased weight and BMI z-scores were associated with decreased connectivity in the functional networks of the brain that involve cognitive control, motivation and reward-based decision making.
“Increased BMI and weight are not only associated with physical health consequences but also with brain health,” Kaltenhauser said. “Our study showed that higher weight and BMI z-scores in 9- and 10-year-olds were associated with changes in macrostructures, microstructures and functional connectivity that worsened brain health.”
Senior author Sam Payabvash, M.D., a neuroradiologist and assistant professor of radiology and biomedical imaging at the Yale School of Medicine, said the study’s findings provide an important mechanistic explanation of other studies that show higher BMI in children is associated with poor cognitive functioning and school performance.
“The longitudinal ABCD study gives us the opportunity to observe any changes that occur in children with higher weight and BMI z-scores,” Dr. Payabvash said. “We’ll need to watch over the next 6 to 10 years.”
Co-authors are Clara Weber, Huang Lin, Ajay Malhotra, M.B.B.S., M.D., R. Todd Constable, Ph.D., Julián N. Acosta, M.D., Guido J. Falcone, M.D., Sarah N. Taylor, M.D., Laura R. Ment, M.D., and Kevin N. Sheth M.D.
Note: Copies of RSNA 2022 news releases and electronic images will be available online at RSNA.org/press22.
RSNA is an association of radiologists, radiation oncologists, medical physicists and related scientists promoting excellence in patient care and health care delivery through education, research and technologic innovation. The Society is based in Oak Brook, Illinois. (RSNA.org)
Editor’s note: The data in these releases may differ from those in the published abstract and those actually presented at the meeting, as researchers continue to update their data right up until the meeting. To ensure you are using the most up-to-date information, please call the RSNA Newsroom at 1-312-791-6610.
For patient-friendly information on brain MRI, visit RadiologyInfo.org.
Video (MP4):

Video 3. Simone Kaltenhauser discusses her research on how obesity in children is link to poor brain health.
Download MP4
(Right-click and Save As)
Images (JPG, TIF):
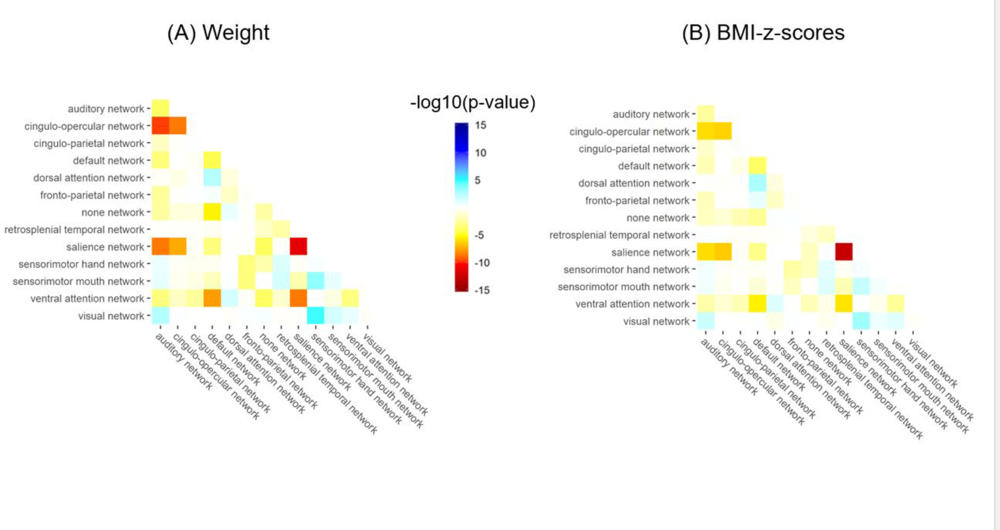
Figure 1. The connectivity of functional networks is associated with weight and BMI variations. Most affected are the so-called “salience” and “cingulo-opercular” networks that are related to inhibitory control, motivation and reward-based decision making. Blue is used for positive and red for negative associations.
High-res (TIF) version
(Right-click and Save As)
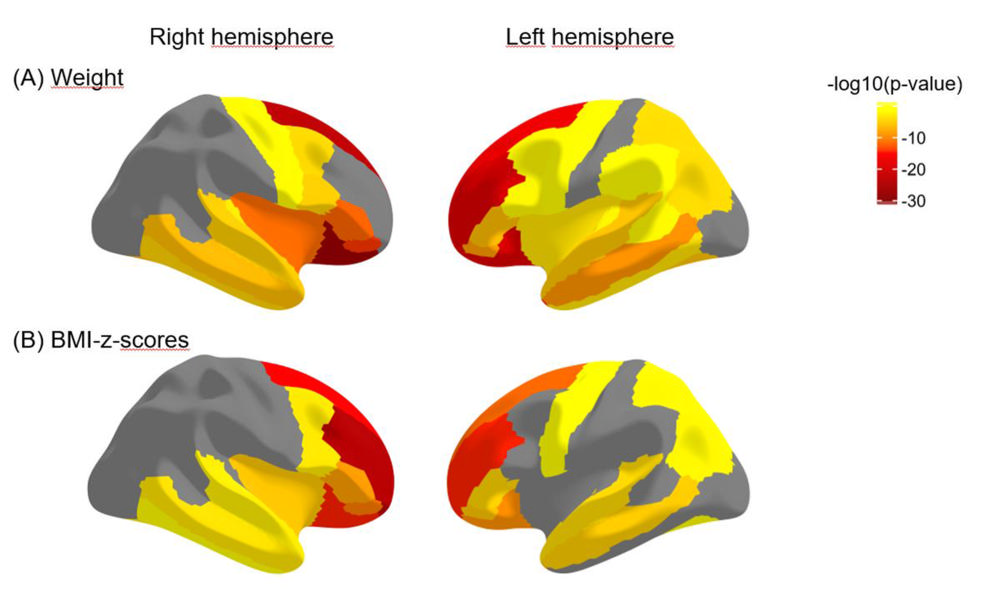
Figure 2. The cortical thickness of prefrontal regions is negatively associated with weight and BMI measurements, meaning that higher weight and BMI are related to lower cortical thickness.
High-res (TIF) version
(Right-click and Save As)
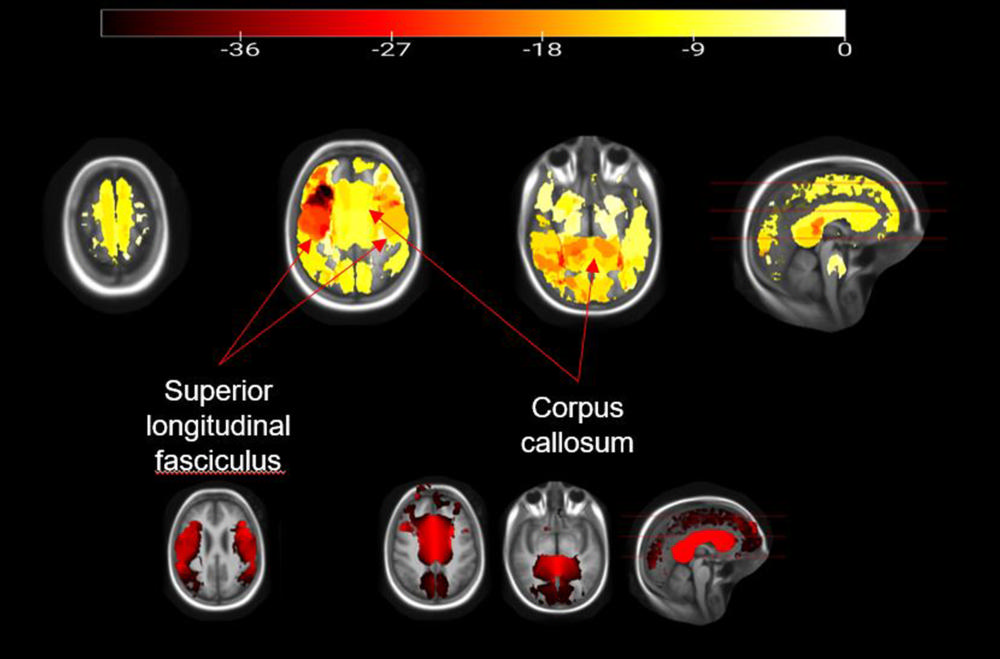
Figure 3. The integrity of the white matter is extensively impaired with higher BMI in children. Most affected are the corpus callosum, which is the main connector of both brain hemispheres, and the superior longitudinal fasciculus that connects several (frontal, occipital, parietal and temporal) lobes.
High-res (TIF) version
(Right-click and Save As)
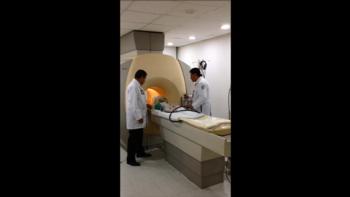
Figure 4. Child undergoing pediatric MRI (Courtesy of RadiologyInfo.org)
High-res (TIF) version
(Right-click and Save As)
Powerpoint:
(Right-click and Save As)
Additional Resources