RSNA Press Release
- Carotid artery stenting not only helps prevent stroke, it speeds up the brain's thought process.
- Stenting is a minimally invasive procedure that effectively treats narrowing of the carotid arteries.
Carotid Artery Stenting Improves Thought Process
Released: November 28, 2005
| Media Contacts: | |
| RSNA Media Relations: | (630) 590-7762 |
| Maureen Morley (630) 590-7754 mmorley@rsna.org |
Heather Babiar (630) 590-7738 hbabiar@rsna.org |
CHICAGO - Stenting of the carotid artery significantly improves cognitive speed and may improve memory function in some patients, according to research presented today at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
"To my knowledge this is the first study combining neuropsychological testing and perfusion imaging that screens for silent ischemic stroke events that can occur during stenting," said Iris Q. Grunwald, M.D., consultant at Saarland University Clinic in Homburg, Germany.
Stroke is the third leading cause of death in the United States. Every year, approximately 600,000 Americans experience a stroke, one-quarter of which are caused by carotid arterial occlusive disease, or a narrowing of the carotid arteries. Until recently, surgery was the standard treatment for this disease, but carotid artery stenting has emerged as an accepted minimally invasive alternative to restore blood flow to the brain.
To perform the procedure, an interventional radiologist inserts a long catheter into a tiny incision in the common femoral artery in the leg. Using an image-guidance system such as computed tomography (CT) and a guide wire, the radiologist positions the sheath at the site of the narrowing, or stenosis, in the carotid artery, expands the artery with a balloon and inserts a stent to hold the artery open.
While stenting is known to be an effective treatment for stroke prevention, little is known on the treatment's effects on cognitive function.
Dr. Grunwald and colleagues performed carotid artery stenting on 26 patients. All were given neuropsychological tests at least 24 hours before and three months after the stenting procedure. These tests included tests for cognitive speed (how quickly the brain processes information) and memory function. Patients were also tested for dementia and depression. The researchers examined the patients with diffusion- and perfusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) before and after stenting.
The results showed that cognitive speed increased significantly after stenting, regardless of the patient's age or the severity of the stenosis. In addition, the researchers found a correlation between the degree of vessel stenosis and perfusion deficit, or decreased blood flow, in the brain area on the side of the stenosis. Increasing the blood flow by stenting resulted in an increase in memory function in patients with perfusion deficit.
"Stenting is a safe way to treat carotid artery stenosis," Dr. Grunwald said. "In addition, stenting of the carotid artery may offer more than reduced stroke risk, especially to patients with impaired brain perfusion."
Co-authors are Wolfgang Reith, M.D., Tillman Supprian, M.D., Peter Falkai, M.D., Christoph Krick, Ph.D., Tobias Struffert, M.D., Kathrin Zercher, Verena Fedder and Friederike Winnemann.
# # #
Note: Copies of RSNA 2005 news releases and electronic images will be available online at RSNA.org/press05 beginning Monday, Nov. 28.
RSNA is an association of more than 38,000 radiologists, radiation oncologists, medical physicists and related scientists committed to promoting excellence in radiology through education and by fostering research, with the ultimate goal of improving patient care. The Society is based in Oak Brook, Ill.
Editor's note: The data in these releases may differ from those in the printed abstract and those actually presented at the meeting, as researchers continue to update their data right up until the meeting. To ensure you are using the most up-to-date information, please call the RSNA Newsroom at (312) 949-3233.
| Abstract: |
Images (.JPG format)
 Figure 1. Photograph of a stent. High-res (TIF) version (Right-click and Save As) |
 Figure 2. Photograph of a stent. High-res (TIF) version (Right-click and Save As) |
 Figure 3. Photograph of equipment used in surgical carotid endarterectomy, which used to be the standard practice. High-res (TIF) version (Right-click and Save As) |
 Figure 4. Photograph of the carotid artery before stenting. High-res (TIF) version (Right-click and Save As) |
 Figure 5. Photograph of the carotid artery after stenting. High-res (TIF) version (Right-click and Save As) |
 Figure 6. Photograph of the medical equipment used in stenting (catheter and guide wire). High-res (TIF) version (Right-click and Save As) |
 Figure 7. Illustration of the stent being modeled to the vessel using a balloon. High-res (TIF) version (Right-click and Save As) |
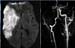 Figure 8. MR image of sudden paresis in a patient’s brain. High-res (TIF) version (Right-click and Save As) |
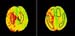 Figure 9. PWI – brain perfusion. High-res (TIF) version (Right-click and Save As) |
 Figure 10. Photograph of the carotid artery after stenting. High-res (TIF) version (Right-click and Save As) |
 Figure 11. Photograph of the carotid artery after stenting. High-res (TIF) version (Right-click and Save As) |
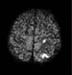 Figure 12. MR Image of the brain showing that there is no neurological defcit after stenting. High-res (TIF) version (Right-click and Save As) |
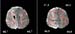 Figure 13. Image of brain, 89% ACI stenosis right, before stent. High-res (TIF) version (Right-click and Save As) |
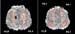 Figure 14. Improvement in cognitive speed, after stent. High-res (TIF) version (Right-click and Save As) |
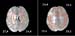 Figure 15. Image of brain, right ICA stenosis>90%, before stent. High-res (TIF) version (Right-click and Save As) |
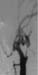 Figure 16. Photograph of the carotid artery before stent. High-res (TIF) version (Right-click and Save As) |
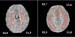 Figure 17. Image of brain, marked improvement after stent concerning cognitive speed, verbal fluency and delayed recall. High-res (TIF) version (Right-click and Save As) |
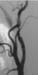 Figure 18. Photograph of the carotid artery after stent. High-res (TIF) version (Right-click and Save As) |
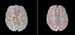 Figure 19. Image of brain, right ICA stenosis, 75%. High-res (TIF) version (Right-click and Save As) |
 Figure 20. Image of brain, only slight change in cognitive function after stent. High-res (TIF) version (Right-click and Save As) |
 PDF
PDF