MRI Technique Detects Evidence of Cognitive Decline Before Symptoms Appear
Released: October 07, 2014
At A Glance
- Noninvasive arterial spin labeling MRI can detect signs of cognitive decline in the brain even before symptoms appear.
- Patients who showed reduced brain perfusion at their initial exams exhibited cognitive decline at follow-up 18 months later.
- Dementia affects more than 35 million people worldwide, a number expected to more than double by 2030.
- RSNA Media Relations
1-630-590-7762
media@rsna.org - Linda Brooks
1-630-590-7738
lbrooks@rsna.org - Emma Day
1-630-590-7791
eday@rsna.org
OAK BROOK, Ill. — A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) technique can detect signs of cognitive decline in the brain even before symptoms appear, according to a new study published online in the journal Radiology. The technique has the potential to serve as a biomarker in very early diagnosis of preclinical dementia.
The World Health Organization estimates that dementia affects more than 35 million people worldwide, a number expected to more than double by 2030. Problems in the brain related to dementia, such as reduced blood flow, might be present for years but are not evident because of cognitive reserve, a phenomenon where other parts of the brain compensate for deficits in one area. Early detection of cognitive decline is critical, because treatments for Alzheimer's disease, the most common type of dementia, are most effective in this early phase.
Researchers recently studied arterial spin labeling (ASL), a promising MRI technique that doesn't require injection of a contrast agent. ASL measures brain perfusion, or penetration of blood into the tissue.
"ASL MRI is simple to perform, doesn't require special equipment and only adds a few minutes to the exam," said study author Sven Haller, M.D., from the University of Geneva in Geneva, Switzerland.
The study group included 148 healthy elderly participants and 65 people with mild cognitive impairment (MCI). The participants underwent brain MRI and a neuropsychological assessment, a common battery of tests used to determine cognitive ability.
Of the 148 healthy individuals, 75 remained stable, while 73 deteriorated cognitively at 18 months clinical follow-up. Those who deteriorated had shown reduced perfusion at their baseline ASL MRI exams, particularly in the posterior cingulate cortex, an area in the middle of the brain that is associated with the default mode network, the neural network that is active when the brain is not concentrating on a specific task. Declines in this network are seen in MCI patients and are more pronounced in those with Alzheimer's disease.
The pattern of reduced perfusion in the brains of healthy individuals who went on to develop cognitive deficits was similar to that of patients with MCI.
"There is a known close link between neural activity and brain perfusion in the posterior cingulate cortex," Dr. Haller said. "Less perfusion indicates decreased neural activity."
The results suggest that individuals with decreased perfusion detected with ASL MRI may temporarily maintain their cognitive status through the mobilization of their cognitive reserve, but will eventually develop subtle cognitive deficits.
Previous research done with positron emission tomography (PET), the current gold standard for brain metabolism imaging, found that patients with Alzheimer's disease had reduced metabolism in the same area of the brain where the perfusion abnormalities were found using ASL MRI. This points to a close link between brain metabolism and perfusion, according to Dr. Haller.
ASL MRI has potential as a standalone test or as an adjunct to PET for dementia screening, Dr. Haller said. While PET can identify markers of Alzheimer's disease in the brain and cerebrospinal fluid, it exposes the patient to radiation. ASL does not expose the patient to radiation and is easy to perform in routine clinical settings.
"ASL might replace the classic yet unspecific fluordesoxyglucose PET that measures brain metabolism. Instead, PET could be done with the new and specific amyloid PET tracers," Dr. Haller said.
The results also support a role for ASL MRI as an alternative to neuropsychological testing.
The researchers plan to perform follow-up studies on the patient group to learn more about ASL and long-term cognitive changes.
"Arterial Spin Labeling May Contribute to the Prediction of Cognitive Deterioration in Healthy Elderly Individuals." Collaborating with Dr. Haller were Aikaterini Xekardaki, M.D., Cristelle Rodriguez, M.Sc., Marie-Louise Montandon, Ph.D., Simona Toma, M.Sc., Eline Tombeur, B.Sc., François R. Herrmann, M.D., Dina Zekry, M.D., Karl-Olof Lovblad, M.D., Frederik Barkhof, M.D., and Panteleimon Giannakopoulos, M.D.
Radiology is edited by Herbert Y. Kressel, M.D., Harvard Medical School, Boston, Mass., and owned and published by the Radiological Society of North America, Inc. (http://radiology.rsna.org/)
RSNA is an association of more than 53,000 radiologists, radiation oncologists, medical physicists and related scientists, promoting excellence in patient care and health care delivery through education, research and technologic innovation. The Society is based in Oak Brook, Ill. (RSNA.org)
For patient-friendly information on MRI of the brain, visit RadiologyInfo.org.
Images (.JPG and .TIF format)
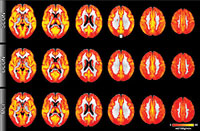
Figure 1. Brain perfusion. Red indicates low perfusion, yellow indicates high perfusion. Overall, the brain perfusion is similar between all three groups. The most prominent difference is present in the posterior cingulate cortex (indicated by the arrow), a region close to the midline in the superior and posterior part of the brain. Control participants who remain stable have higher perfusion as compared to deteriorating controls and MCI.
High-res (TIF) version
(Right-click and Save As)
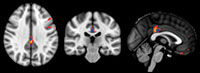
Figure 2. Illustrates the direct comparison between the different groups. The biggest difference is present between stable controls and MCI, indicated in red-yellow, notably in the posterior cingulate cortex. The comparison of stable versus deteriorating controls (blue) shows differences in the same region yet less pronounced. The comparison between deteriorating controls and MCI revealed no significant differences.
High-res (TIF) version
(Right-click and Save As)
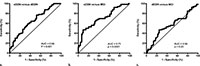
Figure 3. ROC curve analysis of the pairwise comparison between groups. ASL relative CBF in PCC enabled discrimination of (a) dCON (P ˂ .001) and (b) MCI (P˂ .001) from sCON; however, there was no difference between (c) dCON and MCI.
High-res (TIF) version
(Right-click and Save As)
