Lung Abnormalities Seen in Children and Teens with Long COVID
Released: February 25, 2025
- RSNA Media Relations
1-630-590-7762
media@rsna.org - Linda Brooks
1-630-590-7738
lbrooks@rsna.org
OAK BROOK, Ill. — An advanced type of MRI uncovers significant lung abnormalities in children and adolescents with long COVID, according to a new study published today in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Post-COVID-19 condition, commonly known as long COVID, can affect individuals of all ages and is diagnosed when symptoms persist for more than 12 weeks after an initial COVID-19 infection. Children and adolescents typically experience a milder form of the condition, but common symptoms such as chronic fatigue, headaches and poor concentration can negatively impact school performance and social activities.
While chest CT is frequently used to diagnose and monitor lung function of adults with long COVID, it is not typically recommended in children because it exposes the patient to ionizing radiation and may require injection of a contrast agent.
Young patients with suspected long COVID are typically evaluated with pulmonary function tests, echocardiography and reviews of medical history. Unfortunately, conventional pulmonary tests often show normal lung and cardiac function, even in symptomatic patients.
“Parents should understand that their children’s persistent symptoms after COVID-19 may have a measurable physiological basis, even when standard medical tests appear normal,” said lead study author Gesa H. Pöhler, M.D., a senior physician in the Department of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology at Hannover Medical School in Germany.
The researchers employed phase-resolved functional lung (PREFUL) MRI. This advanced MRI technology can analyze lung ventilation (air movement in and out of the lungs) and perfusion (blood flow through the lungs). PREFUL MRI doesn’t require the use of radiation or intravenous contrast agents and can be done while the patient breathes freely, making it a suitable procedure for children.
“Our research provides the first comprehensive evidence of measurable regional lung perfusion abnormalities in pediatric post-COVID-19 condition using radiation-free, contrast-free lung imaging,” Dr. Pöhler said.
For the prospective study, conducted between April 2022 and 2023, the researchers enrolled 54 patients ranging in age from 11 to 17 years. Half of the patients were diagnosed with long COVID, and the other half were healthy controls. A self-reported assessment called the bell score was used to assess symptom severity in patients with long COVID.
Compared to healthy controls, children and adolescents with long COVID had significantly reduced blood flow in the lungs. A reduction in blood flow patterns in organs or other areas of the body can result in a lack of sufficient oxygen and nutrients.
The most prevalent symptom of fatigue affected all but one patient with long COVID.
“Importantly, the severity of fatigue symptoms correlated with these blood flow changes, suggesting a possible biological basis for the patients’ ongoing symptoms,” Dr. Pöhler said.
In addition to poor blood flow, a subgroup of long COVID patients with cardiopulmonary symptoms, such as shortness of breath, also showed a reduction of air movement and reach in the lungs.
The researchers suggest that continuous monitoring of lung abnormalities in children with long COVID at various stages of the condition could help guide therapeutic interventions and monitoring strategies.
“Quantitative lung MRI establishes a potential imaging biomarker profiling and helps to enable disease severity follow-up for this complex condition in the future,” Dr. Pöhler said.
“Phase-resolved Functional Lung MRI Reveals Distinct Lung Perfusion Phenotype in Children and Adolescents with Post-COVID-19 Syndrome.” Collaborating with Dr. Pöhler were Andreas Voskrebenzev, Ph.D., Marc-Luca Heinze, Valentina Skeries, M.D., Filip Klimeš, Ph.D., Julian Glandorf, M.D., Jan Eckstein, M.D., Nigar Babazade, Marius Wernz, B.S., Alexander Pfeil, M.D., Gesine Hansen, M.D., Frank K. Wacker, M.D., Jens Vogel-Claussen, M.D., Martin Wetzke, M.D., and Diane Miriam Renz, M.D.
Radiology is edited by Linda Moy, M.D., New York University, New York, N.Y., and owned and published by the Radiological Society of North America, Inc. (https://pubs.rsna.org/journal/radiology)
RSNA is an association of radiologists, radiation oncologists, medical physicists and related scientists promoting excellence in patient care and health care delivery through education, research and technologic innovation. The Society is based in Oak Brook, Illinois. (RSNA.org)
For patient-friendly information on chest MRI, visit RadiologyInfo.org.
Images (JPG, TIF):
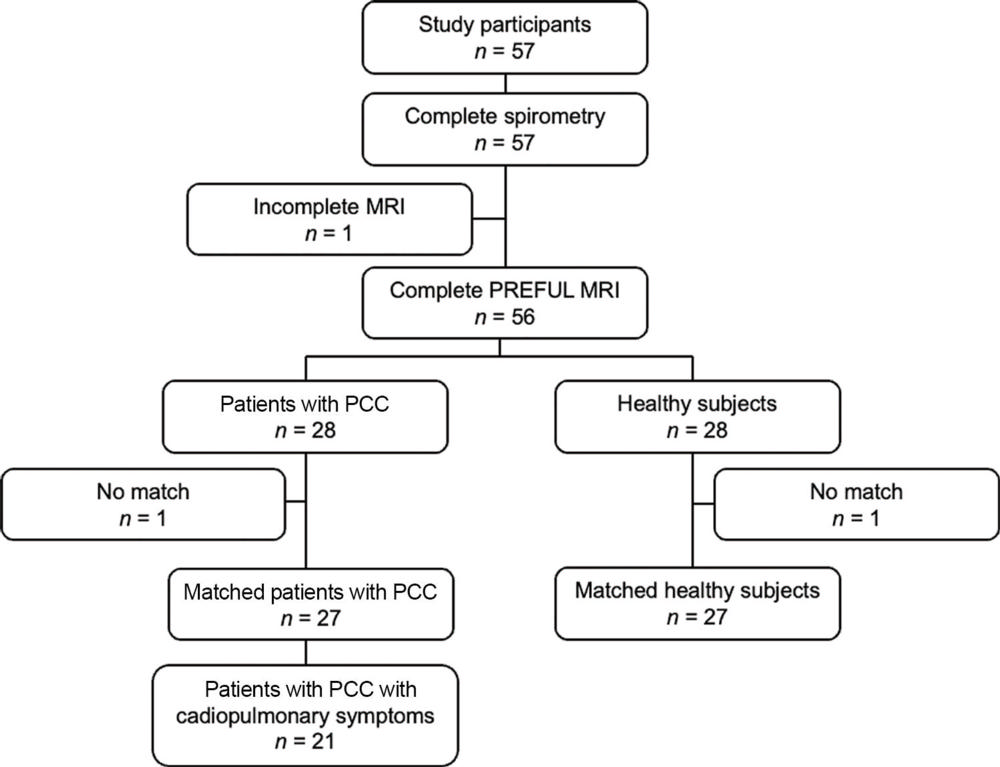
Figure 1. Flowchart summarizes the inclusion process of study participants. PCC = post–COVID-19 condition, PREFUL = phase-resolved functional lung.
High-res (TIF) version
(Right-click and Save As)
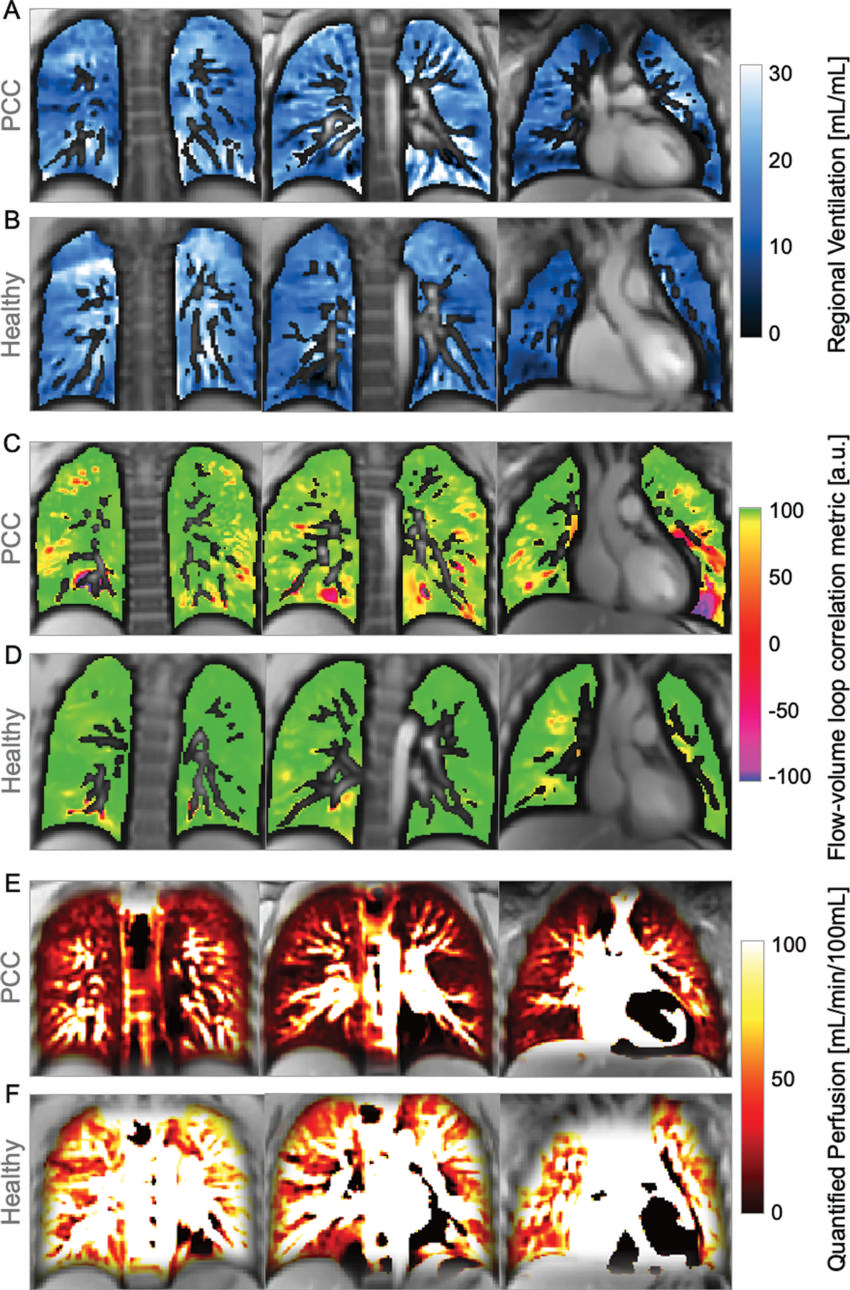
Figure 2. Images show exemplary coronal sections of phase-resolved functional lung MRI ventilation and perfusion maps in a 15-year-old female participant with post–COVID-19 condition (PCC) and in a sex- and age-matched healthy control participant. (A, B) Images show regional ventilation, with values of (A) 0.1 mL/mL in the participant with PCC and (B) 0.5 mL/mL in the healthy control participant. Regarding dynamic ventilation (C, D), images show the flow-volume loop correlation metric, with (C) the participant with PCC at 0.98 arbitrary units (au) and (D) the healthy control participant at 0.99 au. (E, F) Images show perfusion maps depicting a median quantified perfusion of 27 mL/min per 100 mL for the participant with PCC and 89 mL/min per 100 mL for the healthy control participant
High-res (TIF) version
(Right-click and Save As)
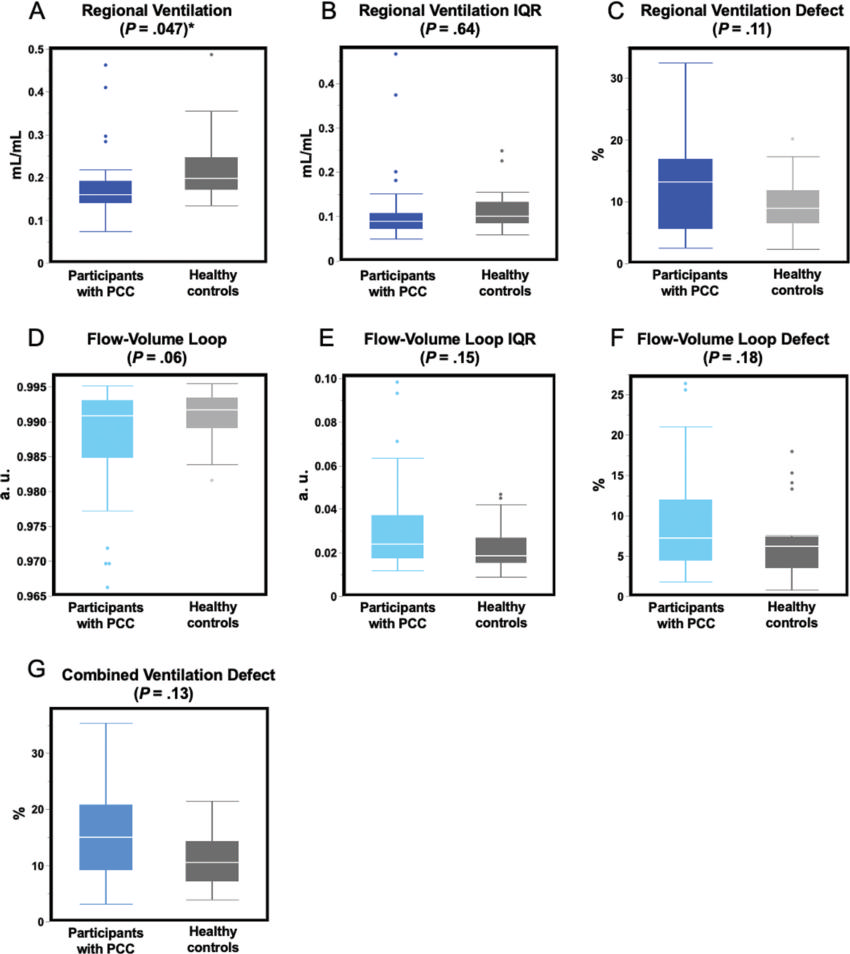
Figure 3. Comparisons of phase-resolved functional lung MRI ventilation parameters between pediatric participants with post–COVID-19 condition (PCC) and healthy control participants. (A–C) Box plots show static ventilation parameters related to regional ventilation. (D–F) Box plots show dynamic ventilation parameters represented by the flow-volume loop correlation metric (FVL-CM). (G) Box plot shows the combination of the defect maps of regional ventilation and FVL-CM. * = Statistically significant differences (P < .05). Corrections for multiple testing were not performed. The line inside each box indicates the median and the box represents the IQR, spanning from the first quartile (the 25th percentile) to the third quartile (the 75th percentile). Whiskers mark the smallest and largest values within 1.5 times the IQR, and points beyond this range are considered outliers. a.u. = arbitrary units.
High-res (TIF) version
(Right-click and Save As)
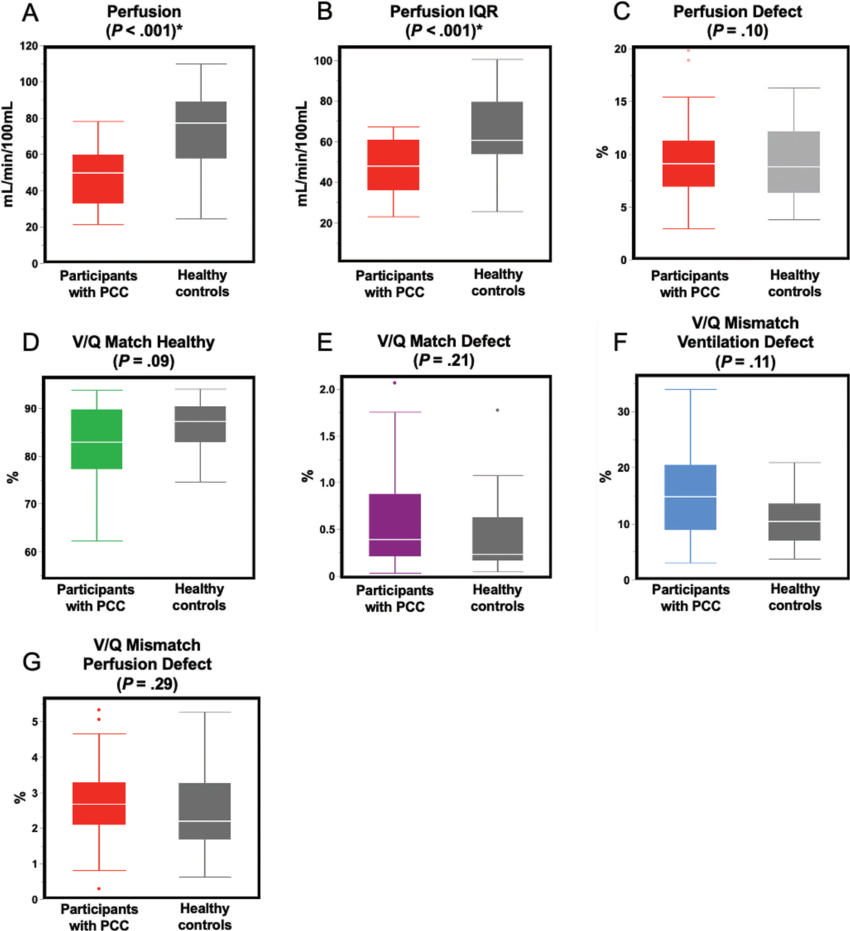
Figure 4. Comparison of phase-resolved functional lung MRI perfusion parameters, ventilation-perfusion (V/Q) matches and V/Q mismatches between pediatric participants with post–COVID-19 condition (PCC) and healthy control participants. Box plots show (A–C) perfusion parameters and (D–G) V/Q matches and mismatches. * Statistically significant differences (P < .05). Corrections for multiple testing were not performed. The line inside each box indicates the median and the box represents the IQR, spanning from the first quartile (the 25th percentile) to the third quartile (the 75th percentile). Whiskers mark the smallest and largest values within 1.5 times the IQR, and points beyond this range are considered outliers. a.u. = arbitrary units.
High-res (TIF) version
(Right-click and Save As)
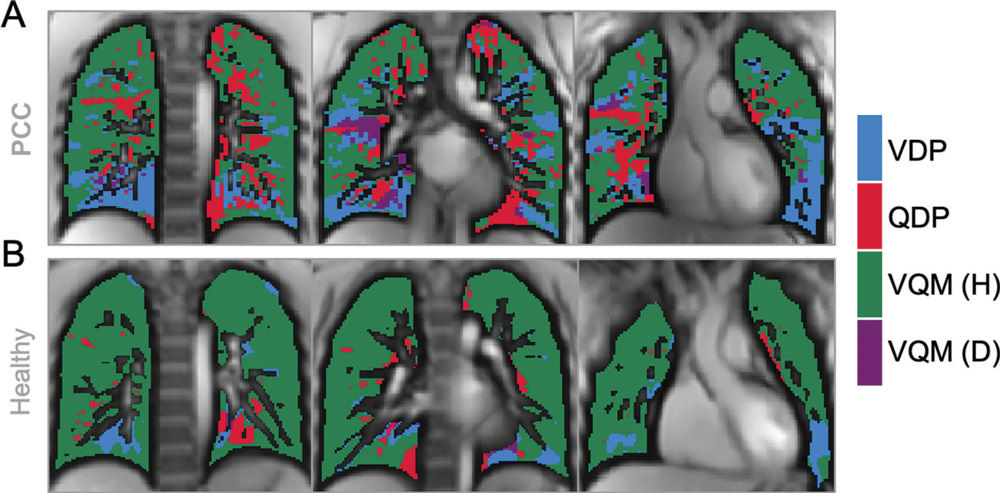
Figure 5. Images show exemplary coronal sections of phase-resolved functional lung MRI defect maps in a pediatric participant with post–COVID-19 condition (PCC) and cardiopulmonary symptoms and a healthy control patient. (A) Images in a 17-year-old male participant with PCC show a ventilation defect percentage (VDP) of 17%, a perfusion defect percentage (QDP) of 16%, a ventilation/perfusion (V/Q) match healthy (VQM [H]) percentage of 64%, and a V/Q mismatch defect (VQM [D]) of 3%. (B) Images in a healthy control participant, with a ventilation defect percentage of 9%, a perfusion defect percentage of 5%, a V/Q match healthy percentage of 86%, and no V/Q mismatch defect.
High-res (TIF) version
(Right-click and Save As)
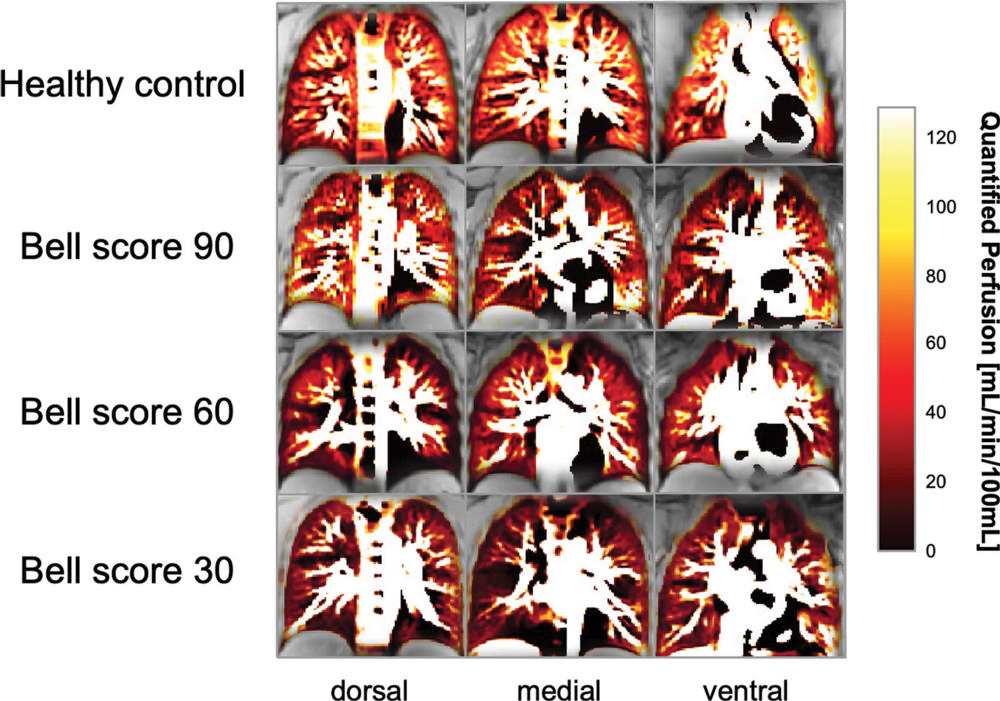
Figure 6. Dorsal, medial, and ventral phase-resolved functional lung MRI perfusion maps show distinct perfusion phenotypes related to the severity of chronic fatigue assessed with the Bell score in three participants with post–COVID-19 condition and in a healthy control participant. The top row shows maps from a 17-year-old male healthy control participant with a median quantified perfusion of 81 mL/min per 100 mL. The second row from the top shows maps from a 17-year-old male participant with a Bell score of 90 and a quantified perfusion of 59 mL/min per 100 mL. The second row from the bottom shows maps from a 16-year-old female participant with a Bell score of 60 with a quantified perfusion of 48 mL/min per 100 mL. The bottom row shows maps from a 15-yearold male participant with a Bell score of 30 and a quantified perfusion of 32 mL/min per 100 mL.
High-res (TIF) version
(Right-click and Save As)
