Deep Learning Model Accurately Diagnoses COPD
Released: December 12, 2024
- RSNA Media Relations
1-630-590-7762
media@rsna.org - Linda Brooks
1-630-590-7738
lbrooks@rsna.org
OAK BROOK, Ill. — Using just one inhalation lung CT scan, a deep learning model can accurately diagnose and stage chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), according to a study published today in Radiology: Cardiothoracic Imaging, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
COPD is a group of progressive lung diseases that impair a person's ability to breathe. Symptoms typically involve shortness of breath and fatigue. There currently is no cure for COPD, and it is the third leading cause of death worldwide, according to the World Health Organization.
A spirometry test, also known as a pulmonary function test, is traditionally used to diagnose COPD. It measures lung function through the quantity of air that can be inhaled and exhaled as well as the speed of exhalation.
CT images of the lungs can aid in COPD diagnosis. The procedure typically requires two image acquisitions, one at full inhalation, called inspiratory, and one at normal exhalation, called expiratory.
"Although studies have recently shown that lung structure, quantitatively measured using lung CT, can supplement COPD severity staging, diagnosis and prognosis, many of these studies require the acquisition of two CT images," said study author Kyle A. Hasenstab, Ph.D., assistant professor of Statistics and Data Science at San Diego State University, California. "However, this type of protocol is not clinically standard across institutions."
Some hospitals are unable to implement expiratory CT protocols due to the added training requirements.
"Implementation of expiratory CT protocols may not be feasible at many institutions due to the need for technologist training to acquire the images and radiologist training to interpret the images," Dr. Hasenstab said.
Additionally, some elderly patients with impaired lung function struggle with holding their breath, as is required during exhalation image acquisition. This may impact the quality of CT images and the accuracy of diagnosis.
Dr. Hasenstab and colleagues hypothesized that a single inhalation CT acquisition combined with a convolutional neural network (CNN), and clinical data would be sufficient for COPD diagnosis and staging. A CNN is a type of artificial neural network that uses deep learning to analyze and classify images.
In this retrospective study, the inhalation and exhalation lung CT images and spirometry data were acquired from 8,893 patients from November 2007 to April 2011. The average age of the patients included in the study was 59 years and all had a history of smoking.
The CNN was trained to predict spirometry measurements using clinical data and either a single-phase or multi-phase lung CT.
The spirometry predictions were then used to predict the Global Initiative for Obstruct Lung Disease (GOLD) stage. The GOLD system classifies the severity of a patient's COPD into one of four stages, with one classified as mild COPD and four classified as very severe COPD.
The results of the study showed that a CNN model developed using only a single respiratory phase CT image accurately diagnosed COPD and was also accurate within one GOLD stage.
The model performed similarly to COPD diagnoses that used combined inhalation and exhalation CT measurements.
"Although many imaging protocols for COPD diagnosis and staging require two CT acquisitions, our study shows that COPD diagnosis and staging is feasible with a single CT acquisition and relevant clinical data," Dr. Hasenstab said.
When clinical data was added, the CNN model's predictions were even more accurate.
CNN models that used only inhalation or exhalation data respectively performed the same. This suggests that certain markers used for COPD diagnosis may overlap across images.
"Reduction to a single inspiratory CT acquisition can increase accessibility to this diagnostic approach while reducing patient cost, discomfort and exposure to ionizing radiation," Dr. Hasenstab said.
"Evaluating the Cumulative Benefit of Inspiratory CT, Expiratory CT, and Clinical Data for COPD Diagnosis and Staging through Deep Learning." Collaborating with Dr. Hasenstab were Amanda N. Lee, B.S., and Albert Hsiao, M.D., Ph.D.
Radiology: Cardiothoracic Imaging is edited by Suhny Abbara, M.D., University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, and owned and published by the Radiological Society of North America, Inc. (https://pubs.rsna.org/journal/cardiothoracic)
RSNA is an association of radiologists, radiation oncologists, medical physicists and related scientists promoting excellence in patient care and health care delivery through education, research, and technologic innovation. The Society is based in Oak Brook, Illinois. (RSNA.org)
For patient-friendly information on chest CT, visit RadiologyInfo.org.
Images (JPG, TIF):
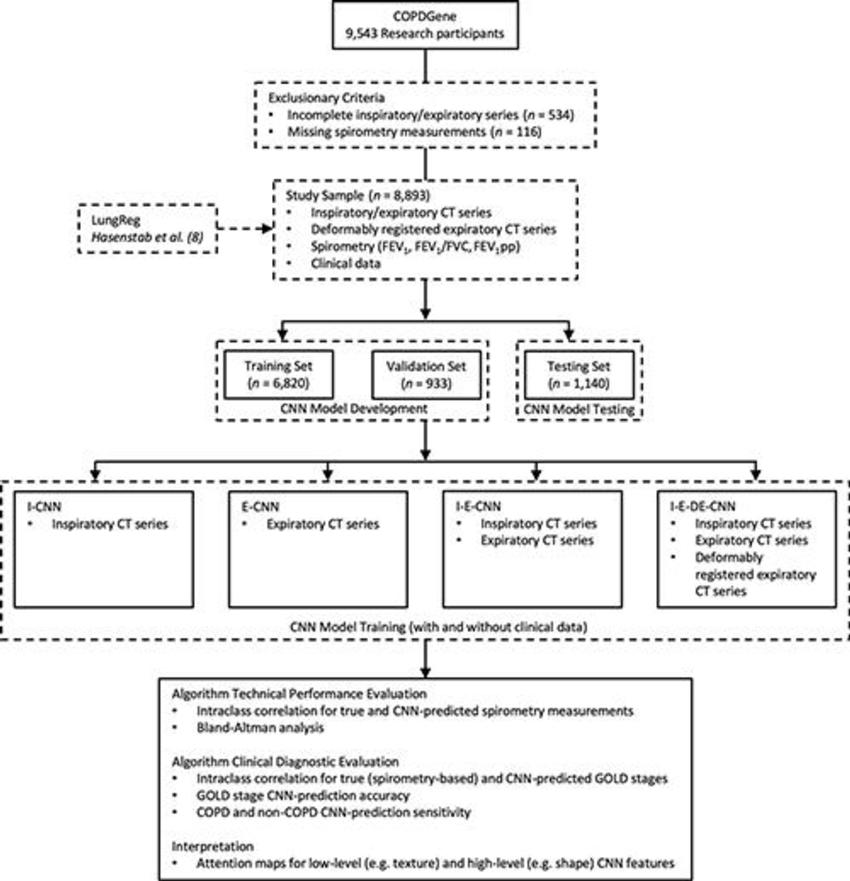
Figure 1. Flowchart of participant selection and study design. CNN = convolutional neural network, COPD = chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, DE = deformably registered expiratory CT image, E = expiratory CT image, FEV1 = forced expiratory volume in 1 second, FEV1pp = forced expiratory volume in 1 second percent predicted, FVC = forced vital capacity, GOLD = Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease, I = inspiratory CT image.
High-res (TIF) version
(Right-click and Save As)
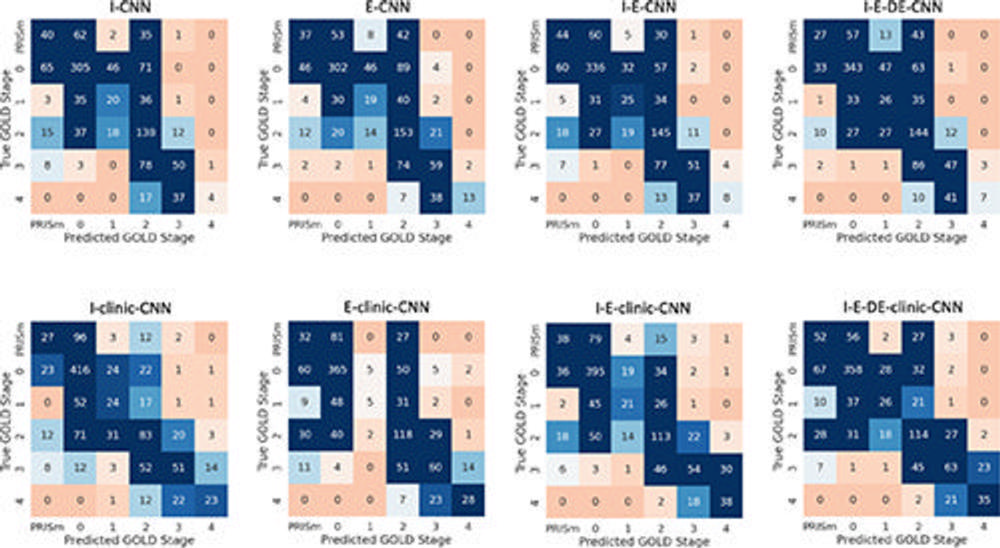
Figure 2. Confusion matrices show accuracy of Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) stage predictions by the different convolutional neural network (CNN) models. Box values indicate the number of predicted samples according to their respective predicted and true GOLD stages. Therefore, box values along the main diagonal indicate the number of times the predicted GOLD stage matched the true GOLD stage. A perfect model would have only high-valued (ie, dark-blue) boxes across the main diagonal and zero-valued (ie, dark-orange) boxes in all other spaces. Model names are abbreviated based on model input. Clinic = clinical data, DE = deformably registered expiratory CT image, E = expiratory CT image, I = inspiratory CT image, PRISm = preserved ratio impaired spirometry.
High-res (TIF) version
(Right-click and Save As)
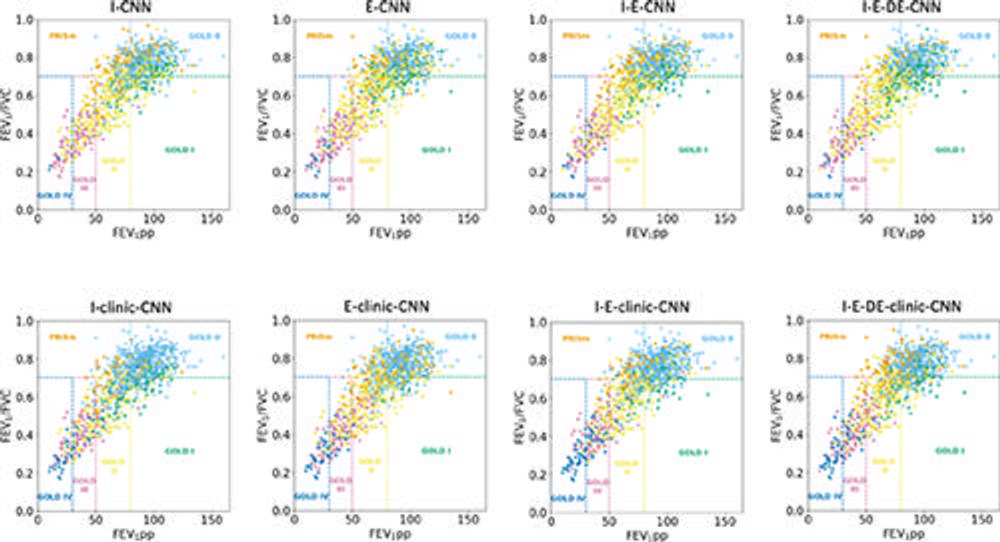
Figure 3. Graphs show relationship between spirometry-based Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) stages from true and convolutional neural network (CNN)–predicted spirometric values. Spirometric values are stratified to show true GOLD stage, while points are colored by CNN-predicted GOLD stage. Model names are abbreviated based on model input. Clinic = clinical data, DE = deformably registered expiratory CT image, E = expiratory CT image, FEV1 = forced expiratory volume in 1 second, FEV1pp = forced expiratory volume in 1 second percent predicted, FVC = forced vital capacity, I = inspiratory CT image, PRISm = preserved ratio impaired spirometry.
High-res (TIF) version
(Right-click and Save As)
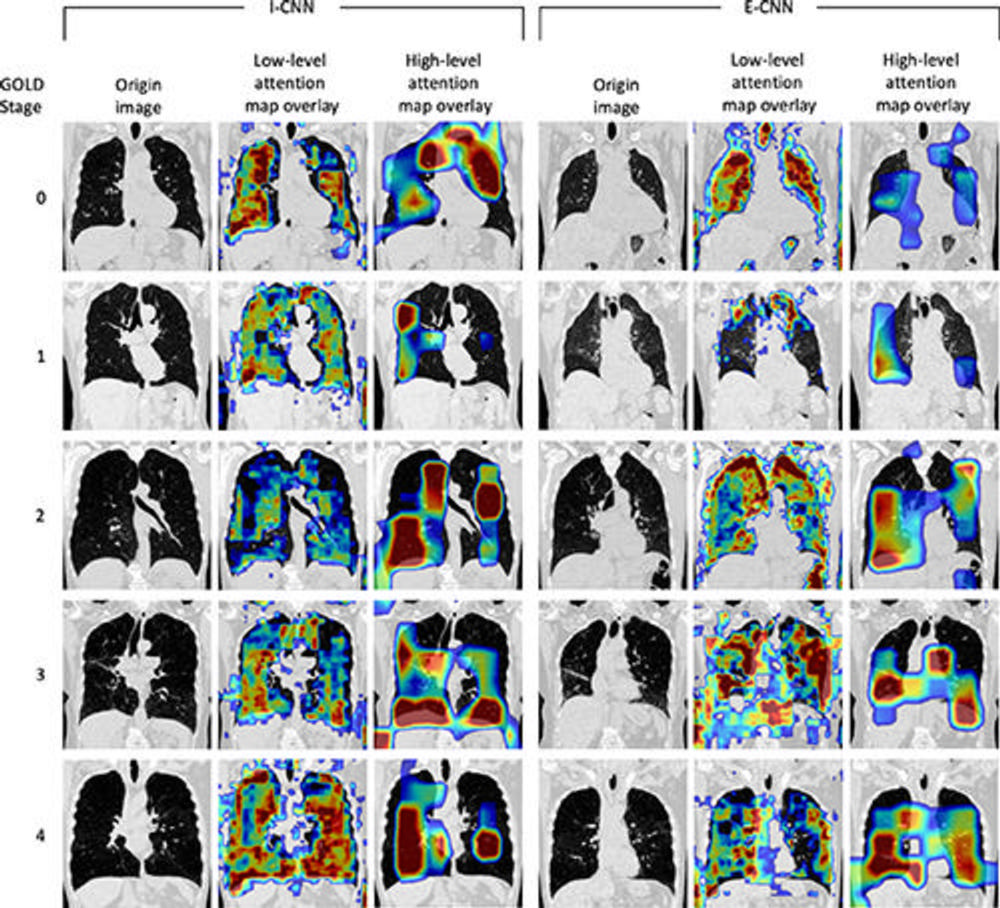
Figure 4. Visualization of attention maps from the residual attention networks for the inspiratory convolutional neural network (I-CNN) and expiratory convolutional neural network (E-CNN) models. Attention maps highlight regions of the input image contributing to the network’s predictions. Low-level features (minor details, such as texture) and high-level features (major details, such as shape) are displayed overlaying a single coronal section of the original input noncontrast CT images. Overlay color indicates strength of attention (ie, strength of contribution) ranging from low attention (blue) to high attention (dark red). One example for each Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) stage is shown.
High-res (TIF) version
(Right-click and Save As)
