Researchers Develop New Coronary Risk Score for Women
Released: December 05, 2024
- RSNA Media Relations
1-630-590-7762
media@rsna.org - Linda Brooks
1-630-590-7738
lbrooks@rsna.org
OAK BROOK, Ill. — A new risk score accurately predicts and categorizes the risk of major adverse cardiovascular events, such as heart attack, in women. The findings were published today in Radiology: Cardiothoracic Imaging, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, heart disease is the leading cause of death in U.S. women. The same can be said for women in Latin America, Europe, Asia and Pacific countries. However, since men are more likely to suffer from heart conditions such as coronary artery disease, women tend to be overlooked in cardiovascular studies.
"Women are often underrepresented in research studies, and in some settings may be excluded," said study lead author Guillermo Romero-Farina, M.D., Ph.D., cardiologist and senior researcher at the Vall d'Hebron University Hospital, Vall d'Hebron Research Institute and CIBERCV in Barcelona, Spain. "Risk stratification in women is particularly important because the clinical presentation of coronary disease in women may differ from that in men and is often atypical."
Coronary risk stratification models are an important tool physicians use to identify which patients are most likely to experience major adverse cardiovascular events, such as heart attack, stroke or even death. Establishing a Coronary Risk Score in Women (CORSWO) may aid in the prediction of major cardiovascular events.
In this retrospective study, Dr. Romero-Farina and colleagues analyzed the data of 2,226 women aged 40 to 93 years who were referred to the Nuclear Cardiology Unit at Vall d'Hebron University Hospital for risk assessment and evaluation.
All patients underwent gated SPECT myocardial perfusion imaging, which is an imaging procedure that measures left ventricular function and myocardial perfusion at the same time.
The average follow-up time occurred around was approximately four years. The maximum follow-up time was 10 years, and all follow-ups occurred in the hospital as a result of a major adverse cardiovascular event.
Using eight variables, the CORSWO calculated the risk of a cardiac event in patients and categorized them into four risk levels: low, moderate, high and very high.
"By grouping patients into different risk levels—ranging from low to very high risk—doctors can better focus resources and treatments on those who need them the most," Dr. Romero-Farina said.
The model accurately predicted major adverse cardiovascular events in women who were categorized as high and very high risk and performed better than other risk models.
The researchers note that this novel approach of incorporating clinical, exercise and imaging-based variables is important in accurately calculating the risk of cardiac events in women.
"The study provides additional insights into identifying high risk or very high-risk women," Dr. Romero-Farina said. "This approach helps us catch potential heart issues earlier, especially serious events like heart attacks and sudden cardiac death, which are the outcomes cardiologists are most concerned about preventing."
"Prediction of Major Adverse Coronary Events Using the Coronary Risk Score in Women." Collaborating with Dr. Romero-Farina were Santiago Aguadé-Bruix, M.D., and Ignacio Ferreira-González, M.D., Ph.D.
Radiology: Cardiothoracic Imaging is edited by Suhny Abbara, M.D., University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, and owned and published by the Radiological Society of North America, Inc. (https://pubs.rsna.org/journal/cardiothoracic)
RSNA is an association of radiologists, radiation oncologists, medical physicists and related scientists promoting excellence in patient care and health care delivery through education, research, and technologic innovation. The Society is based in Oak Brook, Illinois. (RSNA.org)
For patient-friendly information on cardiac imaging, visit RadiologyInfo.org.
Images (JPG, TIF):
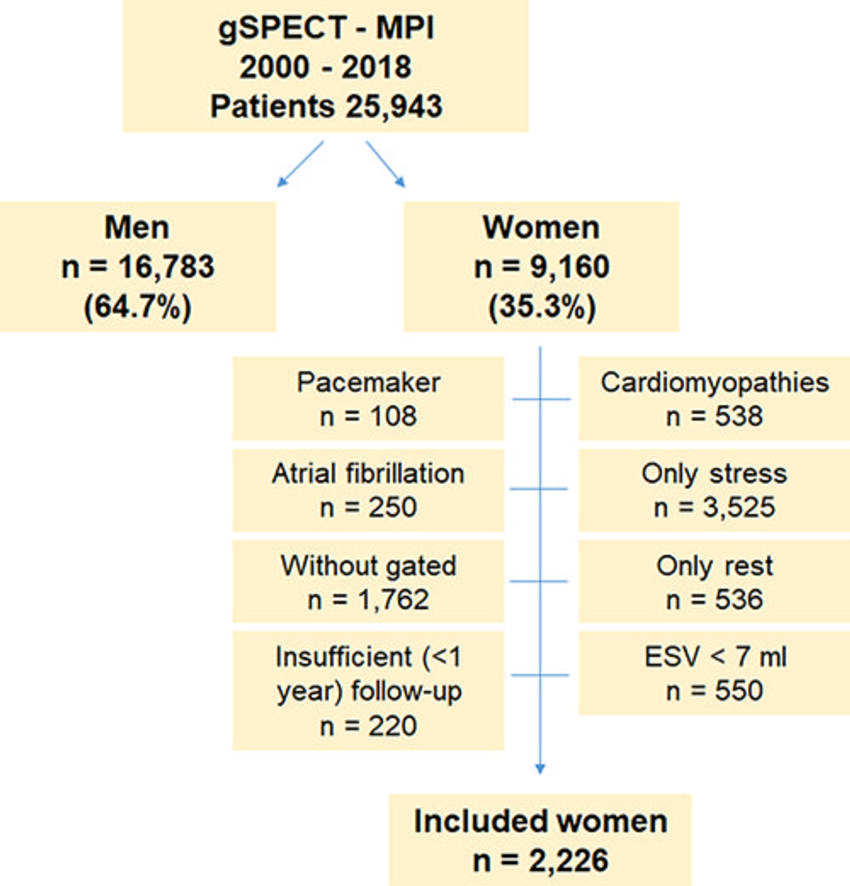
Figure 1. Flow diagram shows female individuals included in the study. ESV = end-systolic volume, gSPECT MPI = gated SPECT myocardial perfusion imaging.
High-res (TIF) version
(Right-click and Save As)
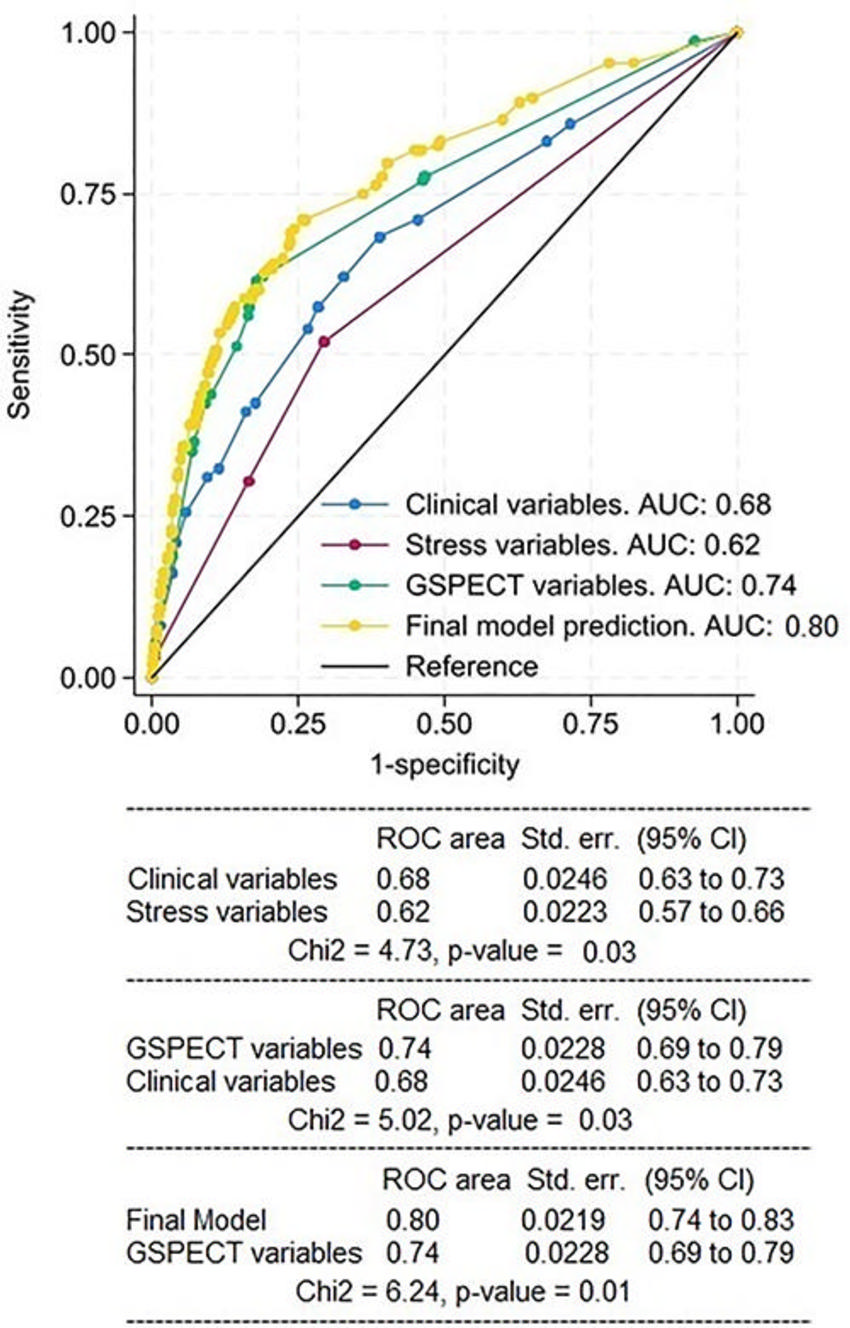
Figure 2. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves for internal validation of the predictor clinical model, stress model, gated SPECT (GSPECT) model, and final model to predict major adverse cardiovascular events. The clinical model was more predictive than the stress model, and the final model had a moderate area under the ROC curve (AUC). Std. err. = standard error.
High-res (TIF) version
(Right-click and Save As)
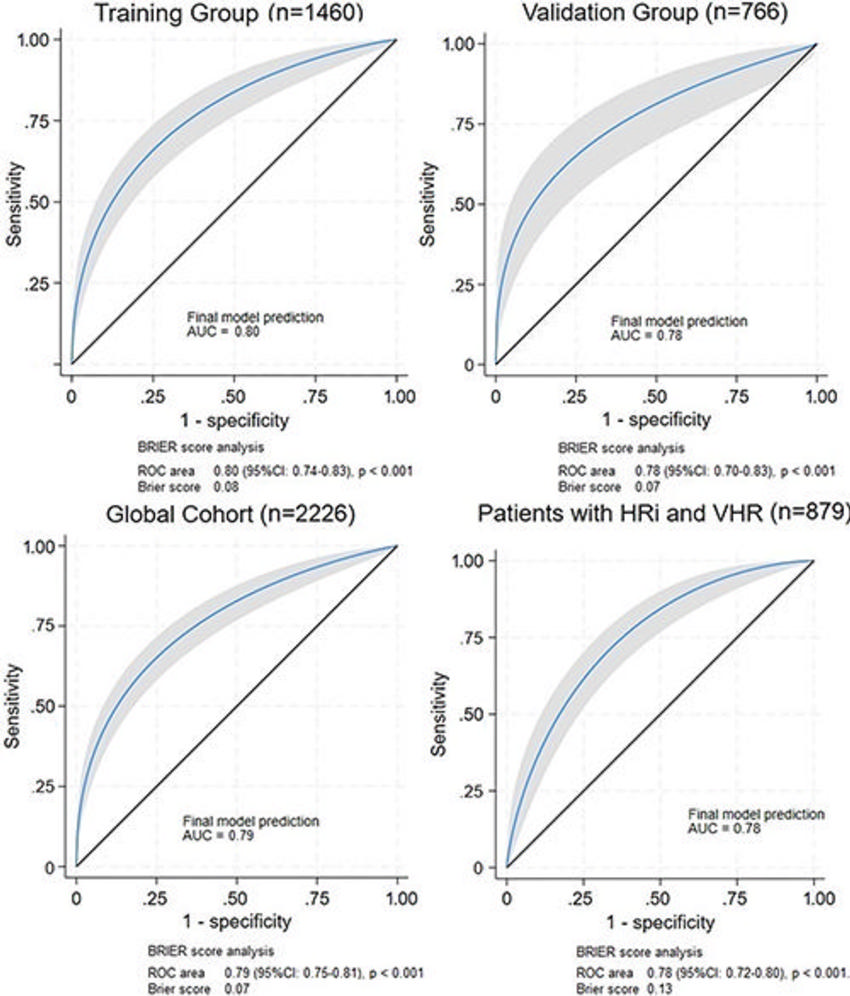
Figure 3. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves analysis to evaluate the ability of the final model to predict major adverse cardiovascular events in the training group (n = 1460), validation group (n = 766), global cohort (n = 2226), and in patients with high risk (HRi) and very high risk (VHR) (n = 879) shows a moderate predictive value. AUC = area under the ROC curve.
High-res (TIF) version
(Right-click and Save As)
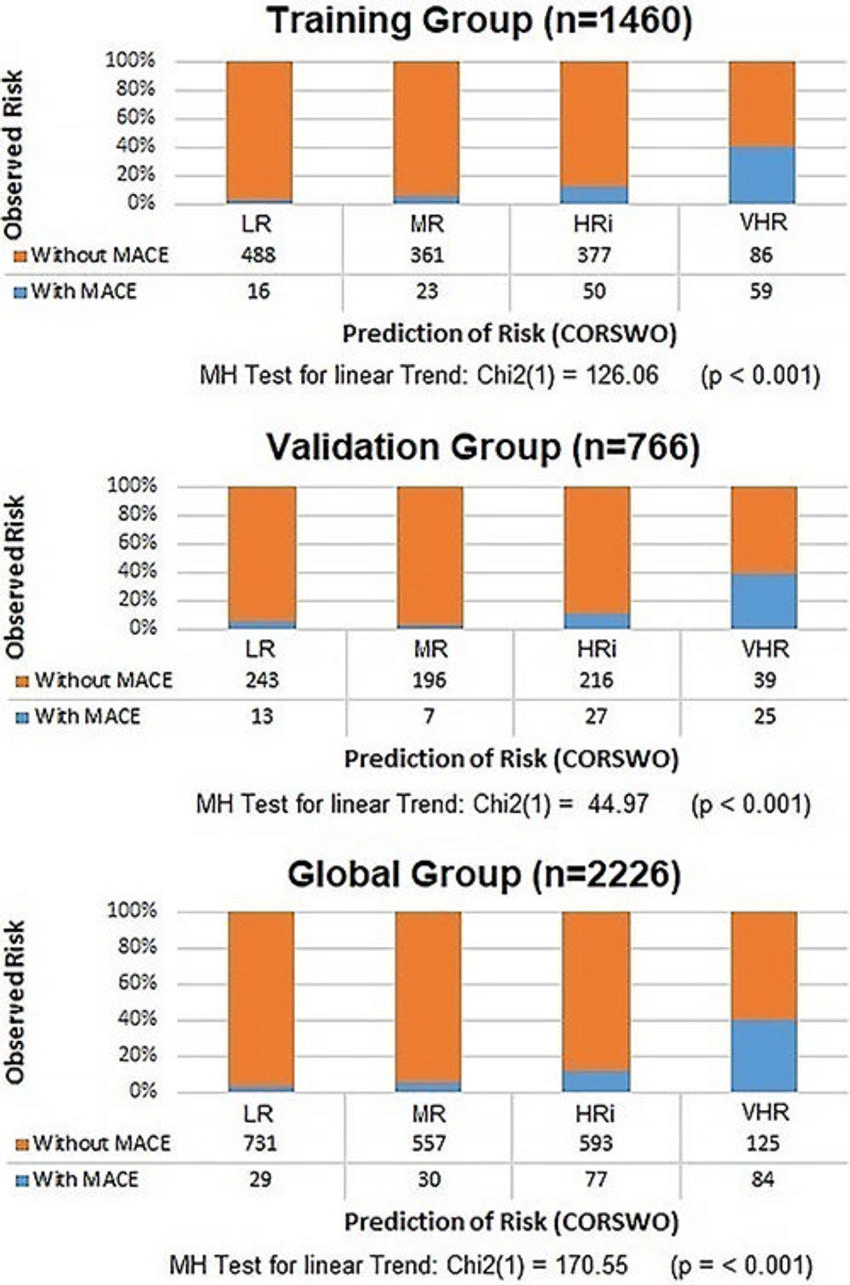
Figure 4. COronary Risk Score in WOmen (CORSWO) to predict MACE. When increasing the levels of CORSWO (risk prediction) calculated by using z-score, the prevalence of MACE (risk observed) also increases. MR, HRi, and VHR detect 89.18%, 83.32%, and 86.82% of MACE in the training, validation, and global cohorts, respectively. HRi = high risk, LR = low risk, MACE = major adverse coronary events, MH test = Mantel-Haenszel test, MR = moderate risk, VHR = very high risk.
High-res (TIF) version
(Right-click and Save As)
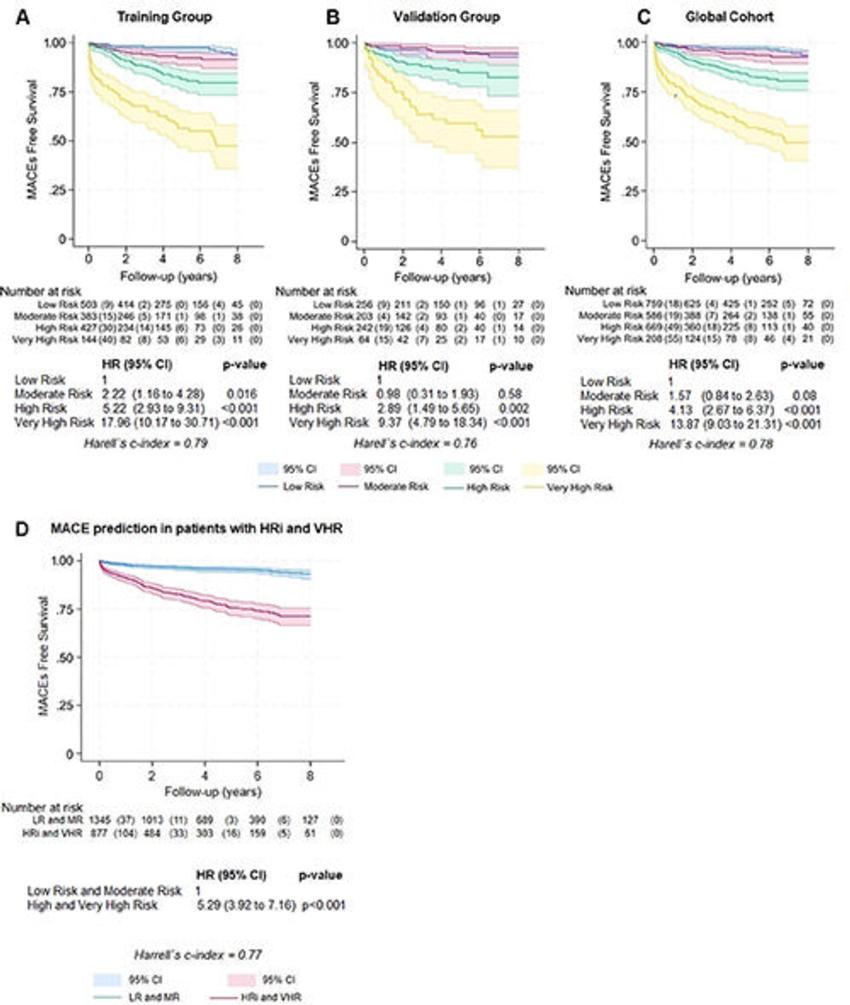
Figure 5. Kaplan-Meier curve analysis. During follow-up after gated SPECT myocardial perfusion imaging, for a one-unit increase in risk level, the MACE incidence rate ratio increases (A) 2.85 (95% CI: 2.42, 3.35; P < .001) in the training group, (B) 2.49 (95% CI: 1.96, 3.15; P < .001) in the validation group, and (C) 2.73 (95% CI: 2.39, 3.12; P < .001) in the global cohort. (D) Patients with high (HRi) and very high (VHR) risk levels (n = 879) are the groups with the worst prognosis. HR = hazard ratio, LR = low risk, MACE = major adverse coronary events, MR = moderate risk.
High-res (TIF) version
(Right-click and Save As)
