Marijuana, Cigarette Smokers at Increased Risk of Emphysema
Released: November 28, 2023
At A Glance
- People who smoke both cigarettes and marijuana are more likely to develop emphysema.
- Combined marijuana and cigarette smokers were also three to four times more likely to have airway wall thickening, which can indicate damage to the airways.
- Marijuana that is smoked is often unfiltered, which can potentially lead to more damaging particles entering the airways and lungs.
- RSNA Media Relations
1-630-590-7762
media@rsna.org - Linda Brooks
1-630-590-7738
lbrooks@rsna.org - Imani Harris
1-630-481-1009
iharris@rsna.org
CHICAGO — Smoking marijuana in combination with cigarettes may lead to increased damage of the lung’s air sacs, according to research being presented today at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
It is commonly believed that smoking marijuana is not harmful to the lungs. There is an abundance of established research that identifies the harms of cigarette smoking. In contrast, very little is known about the effects of marijuana smoking, and even less research has been done on the combined effects of smoking marijuana and cigarettes.
“Marijuana is the most widely used illicit psychoactive substance in the world, and its use has increased in Canada since the legalization of non-medical marijuana in 2018,” said study co-author Jessie Kang, M.D., cardiothoracic radiologist and assistant professor in the Department of Diagnostic Radiology at Dalhousie University in Halifax, Nova Scotia, Canada. “Currently, not much research exists on the effects of marijuana smoking on the lungs.”
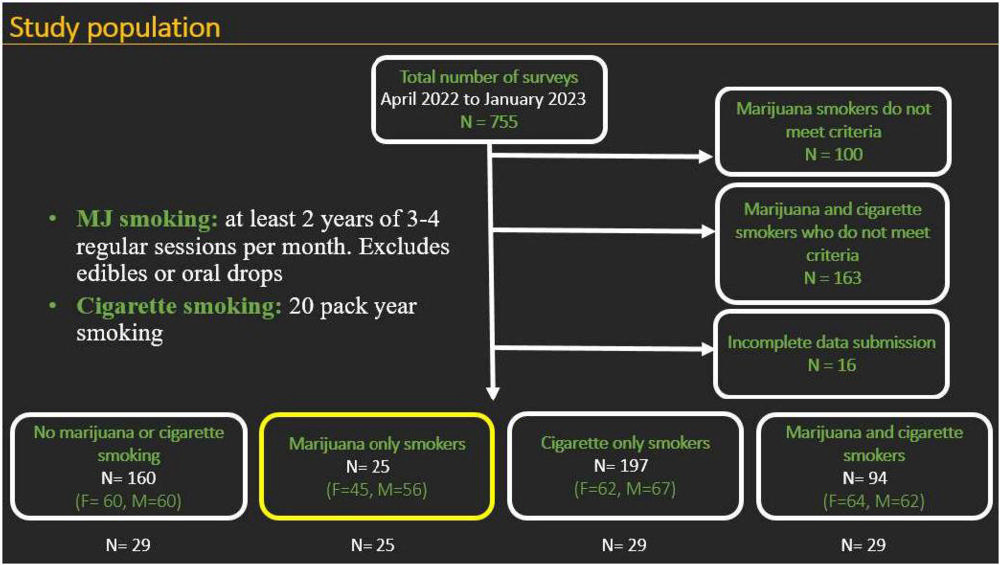
To determine the effects of marijuana and cigarette smoking, researchers for the multicenter prospective study examined the chest CT images of four patient groups: non-smokers, cigarette smokers, marijuana smokers, and combined marijuana and cigarette smokers. Marijuana smokers included in the study had smoked marijuana at least four times a month for two years. Patients who ingested marijuana via edibles or oral drops were excluded from the study.
The researchers found that people who combined marijuana and cigarettes were 12 times more likely to have centrilobular emphysema than non-smokers. Centrilobular emphysema is a type of pulmonary emphysema where the air sacs within the lungs are damaged. This can lead to breathing difficulties and other serious respiratory symptoms.
“The mean number of marijuana smoking years was less than compared to cigarette smokers and combined marijuana and cigarette smokers,” Dr. Kang said. “However, marijuana that is smoked is often unfiltered, which can potentially lead to more damaging particles entering the airways and lungs.”
Combined marijuana and cigarette smokers were three to four times more likely to have airway wall thickening, which can lead to infections, scarring and further airway damage. Association with marijuana only and smoking only with bronchial wall thickening was not as significant. Similar results were seen with centrilobular and paraseptal emphysema, suggesting that the combination of cigarette and marijuana smoking may have a synergistic role on the lungs and airways.
“With our study, we show that there are physical effects of marijuana smoking on the lungs and that cigarette smoking and marijuana smoking may have a combined damaging effect on the lungs,” Dr. Kang said.
According to Dr. Kang, further research is needed to identify the long-term effects of smoking marijuana.
“There is a common public misconception that marijuana smoking is not harmful,” Dr. Kang said. “More research needs to be done in this area, so the public can make an informed decision on their recreational usage of marijuana.”
Co-authors are Sebastian Karpinski, B.Sc., Paul Sathiadoss, M.B.B.S., Eric Lam, M.Sc., Eric Hutfluss, M.D., O. Osorio, M.D., D. A. Hashem, M.D., Matthew D. F. McInnes, M.D., and Giselle Y. Revah, M.D.
Note: Copies of RSNA 2023 news releases and electronic images will be available online at RSNA.org/press23.
RSNA is an association of radiologists, radiation oncologists, medical physicists and related scientists promoting excellence in patient care and health care delivery through education, research and technologic innovation. The Society is based in Oak Brook, Illinois. (RSNA.org)
Editor’s note: The data in these releases may differ from those in the published abstract and those actually presented at the meeting, as researchers continue to update their data right up until the meeting. To ensure you are using the most up-to-date information, please call the RSNA Newsroom at 1-312-791-6610.
For patient-friendly information on chest CT, visit RadiologyInfo.org.
Video (MP4):
Images (JPG, TIF):
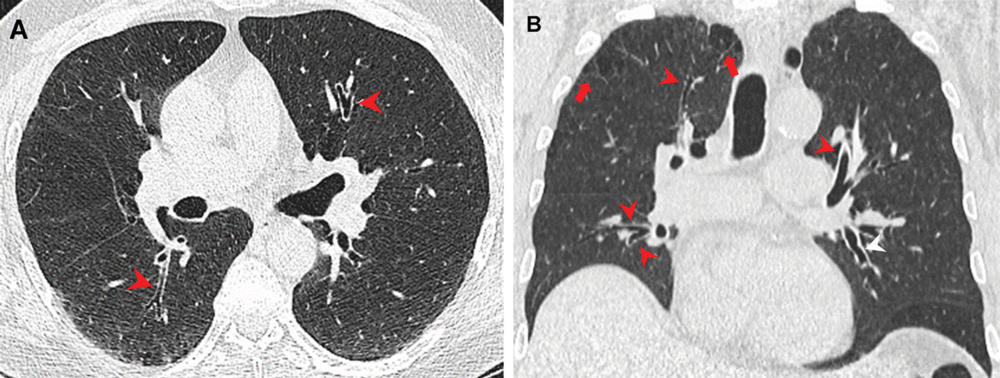
Figure 2. Airway changes in a 66-year-old male marijuana and tobacco smoker with cylindrical bronchiectasis and bronchial wall thickening (arrowheads) in multiple lung lobes in a background of paraseptal and centrilobular emphysema. (Courtesy of Radiology)
High-res (TIF) version
(Right-click and Save As)
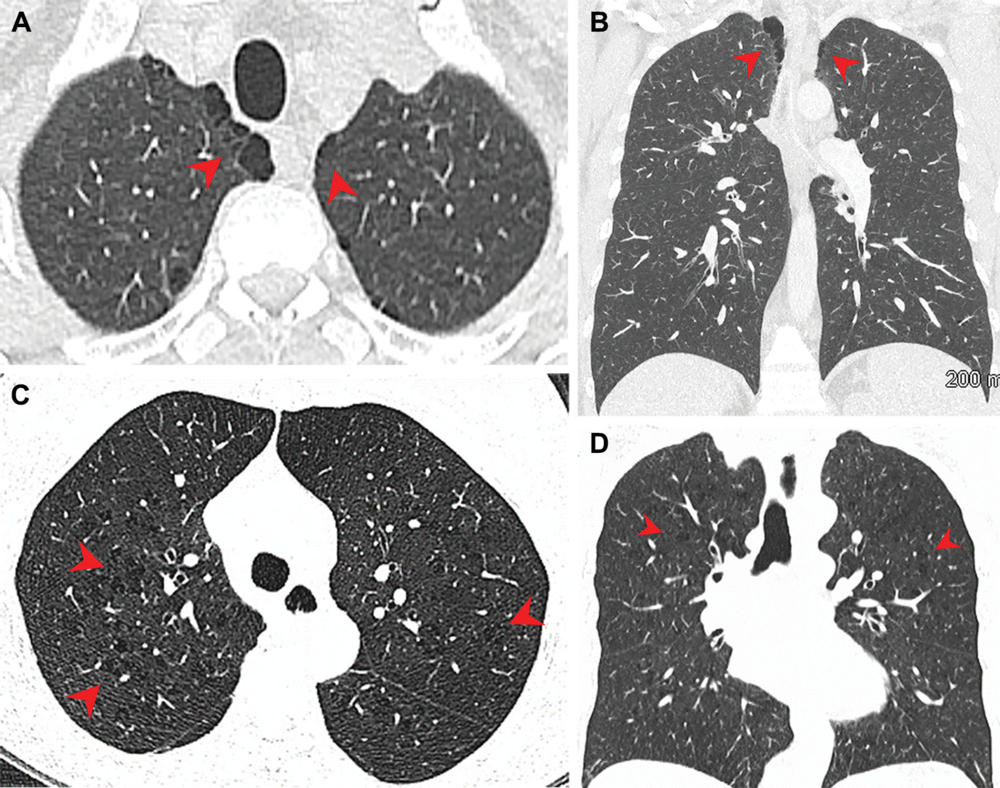
Figure 3. Pulmonary emphysema in marijuana and tobacco smokers. CT images in a male marijuana smoker show paraseptal emphysema in bilateral upper lobes. CT images in a female tobacco smoker with centrilobular emphysema. (Courtesy of Radiology)
High-res (TIF) version
(Right-click and Save As)
Additional Resources