Artificial Intelligence Predicts Alzheimer's Years Before Diagnosis
Released: November 06, 2018
At A Glance
- Artificial intelligence, used in conjunction with FDG-PET, predicted which patients would develop Alzheimer's six years before final diagnosis.
- The AI algorithm was 100 percent accurate in its predictions.
- Timely diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease is extremely important, as treatments and interventions are more effective early in the course of the disease.
- RSNA Media Relations
1-630-590-7762
media@rsna.org - Linda Brooks
1-630-590-7738
lbrooks@rsna.org - Dionna Arnold
1-630-590-7791
darnold@rsna.org
OAK BROOK, Ill. — Artificial intelligence (AI) technology improves the ability of brain imaging to predict Alzheimer's disease, according to a study published in the journal Radiology.
Timely diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease is extremely important, as treatments and interventions are more effective early in the course of the disease. However, early diagnosis has proven to be challenging. Research has linked the disease process to changes in metabolism, as shown by glucose uptake in certain regions of the brain, but these changes can be difficult to recognize.
"Differences in the pattern of glucose uptake in the brain are very subtle and diffuse," said study co-author Jae Ho Sohn, M.D., from the Radiology & Biomedical Imaging Department at the University of California in San Francisco (UCSF). "People are good at finding specific biomarkers of disease, but metabolic changes represent a more global and subtle process."
The study's senior author, Benjamin Franc, M.D., from UCSF, approached Dr. Sohn and University of California, Berkeley, undergraduate student Yiming Ding through the Big Data in Radiology (BDRAD) research group, a multidisciplinary team of physicians and engineers focusing on radiological data science. Dr. Franc was interested in applying deep learning, a type of AI in which machines learn by example much like humans do, to find changes in brain metabolism predictive of Alzheimer's disease.
The researchers trained the deep learning algorithm on a special imaging technology known as 18-F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (FDG-PET). In an FDG-PET scan, FDG, a radioactive glucose compound, is injected into the blood. PET scans can then measure the uptake of FDG in brain cells, an indicator of metabolic activity.
The researchers had access to data from the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI), a major multi-site study focused on clinical trials to improve prevention and treatment of this disease. The ADNI dataset included more than 2,100 FDG-PET brain images from 1,002 patients. Researchers trained the deep learning algorithm on 90 percent of the dataset and then tested it on the remaining 10 percent of the dataset. Through deep learning, the algorithm was able to teach itself metabolic patterns that corresponded to Alzheimer's disease.
Finally, the researchers tested the algorithm on an independent set of 40 imaging exams from 40 patients that it had never studied. The algorithm achieved 100 percent sensitivity at detecting the disease an average of more than six years prior to the final diagnosis.
"We were very pleased with the algorithm's performance," Dr. Sohn said. "It was able to predict every single case that advanced to Alzheimer's disease."
Although he cautioned that their independent test set was small and needs further validation with a larger multi-institutional prospective study, Dr. Sohn said that the algorithm could be a useful tool to complement the work of radiologists—especially in conjunction with other biochemical and imaging tests—in providing an opportunity for early therapeutic intervention.
"If we diagnose Alzheimer's disease when all the symptoms have manifested, the brain volume loss is so significant that it's too late to intervene," he said. "If we can detect it earlier, that's an opportunity for investigators to potentially find better ways to slow down or even halt the disease process."
Future research directions include training the deep learning algorithm to look for patterns associated with the accumulation of beta-amyloid and tau proteins, abnormal protein clumps and tangles in the brain that are markers specific to Alzheimer's disease, according to UCSF's Youngho Seo, Ph.D., who served as one of the faculty advisors of the study.
"If FDG-PET with AI can predict Alzheimer's disease this early, beta-amyloid plaque and tau protein PET imaging can possibly add another dimension of important predictive power," he said.
"A Deep Learning Model to Predict a Diagnosis of Alzheimer Disease Using 18F-FDG PET of the Brain." Collaborating with Drs. Sohn, Franc, and Seo and Ms. Ding were Michael G. Kawczynski, M.S., Hari Trivedi, M.D., Roy Harnish, M.S., Nathaniel W. Jenkins, M.S., Dmytro Lituiev, Ph.D., Timothy P. Copeland, M.P.P., Mariam S. Aboian, M.D., Ph.D., Carina Mari Aparici, M.D., Spencer C. Behr, M.D., Robert R. Flavell, M.D., Ph.D., Shih-Ying Huang, Ph.D., Kelly A. Zalocusky, Ph.D., Lorenzo Nardo, Ph.D., Randall A. Hawkins, M.D., Ph.D., Miguel Hernandez Pampaloni, M.D., Ph.D., and Dexter Hadley, M.D., Ph.D.
Radiology is edited by David A. Bluemke, M.D., Ph.D., University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health, Madison, Wis., and owned and published by the Radiological Society of North America, Inc. (http://radiology.rsna.org/)
RSNA is an association of over 54,000 radiologists, radiation oncologists, medical physicists and related scientists, promoting excellence in patient care and health care delivery through education, research and technologic innovation. The Society is based in Oak Brook, Ill. (RSNA.org)
For patient-friendly information on FDG-PET, visit RadiologyInfo.org.
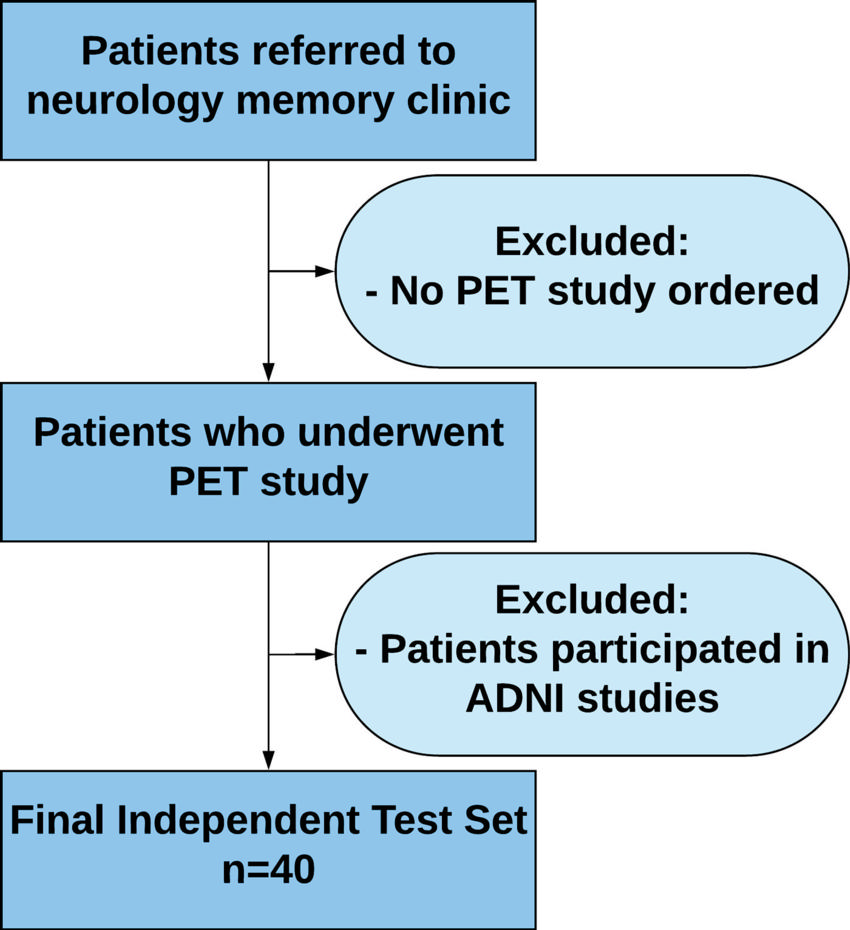
Figure 1. Inclusion and exclusion criteria for the independent test set. Patient must have had at least one follow-up with a neurologist at our local institution. ADNI = Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative.
High-res (TIF) version
(Right-click and Save As)

Figure 2. Example of fluorine 18 fluorodeoxyglucose PET images from Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative set preprocessed with the grid method for patients with Alzheimer disease (AD). One representative zoomed-in section was provided for each of three example patients: A, 76-year-old man with AD, B, 83-year-old woman with mild cognitive impairment (MCI), and, C, 80-year-old man with non-AD/MCI. In this example, the patient with AD presented slightly less gray matter than did the patient with non-AD/MCI. The difference between the patient with MCI and the patient with non-AD/MCI appeared minimal to the naked eyes.
High-res (TIF) version
(Right-click and Save As)
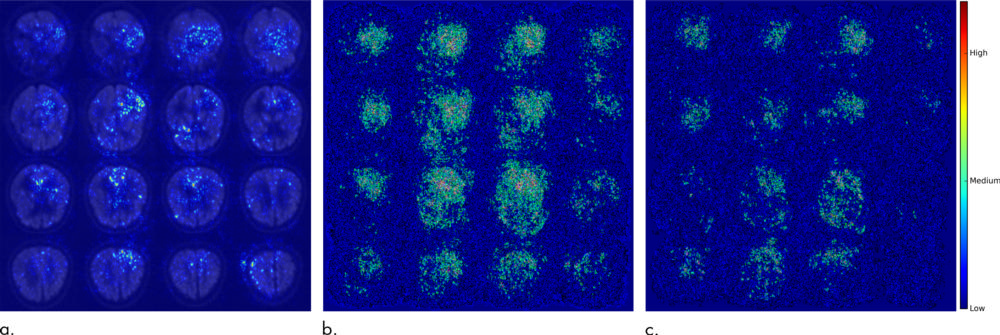
Figure 3. Saliency map of deep learning model Inception V3 on the classification of Alzheimer disease. (a) A representative saliency map with anatomic overlay in 77-year-old man. (b) Average saliency map over 10 percent of Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative set. (c) Average saliency map over independent test set. The closer a pixel color is to the "High" end of the color bar in the image, the more influence it has on the prediction of Alzheimer disease.
High-res (TIF) version
(Right-click and Save As)
