RSNA Press Release
- Stroke patients are benefiting from a novel rehabilitation device that converts their thoughts to electrical impulses to move their upper extremities.
- Even patients who had been diagnosed with severe strokes showed improvement in carrying out activities of daily living following rehabilitation.
- Each year, a new or recurrent stroke occurs in nearly 800,000 people in the U.S.
Novel Rehabilitation Device Improves Motor Skills after Stroke
Released: December 2, 2013
| Media Contacts: | RSNA Newsroom | 1-312-949-3233 |
| Before 11/30/13 or after 12/5/13: | RSNA Media Relations: | 1-630-590-7762 |
| |
Linda Brooks 1-630-590-7738 lbrooks@rsna.org |
Maureen Morley 1-630-590-7754 mmorley@rsna.org |
CHICAGO—Using a novel stroke rehabilitation device that converts an individual's thoughts to electrical impulses to move upper extremities, stroke patients reported improvements in their motor function and ability to perform activities of daily living. Results of the study were presented today at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
"Each year, nearly 800,000 people suffer a new or recurrent stroke in the United States, and 50 percent of those have some degree of upper extremity disability," said Vivek Prabhakaran, M.D., Ph.D., director of functional neuroimaging in radiology at the University of Wisconsin-Madison. "Rehabilitation sessions with our device allow patients to achieve an additional level of recovery and a higher quality of life."
Dr. Prabhakaran, along with co-principal investigator Justin Williams, Ph.D., and a multidisciplinary team, built the new rehabilitation device by pairing a functional electrical stimulation (FES) system, which is currently used to help stroke patients recover limb function, and a brain control interface (BCI), which provides a direct communication pathway between the brain and this peripheral stimulation device.
In an FES system, electrical currents are used to activate nerves in paralyzed extremities. Using a computer and an electrode cap placed on the head, the new BCI-FES device (called the Closed-Loop Neural Activity-Triggered Stroke Rehabilitation Device) interprets electrical impulses from the brain and transmits the information to the FES.
"FES is a passive technique in that the electrical impulses move the patients' extremities for them," Dr. Prabhakaran said. "When a patient using our device is asked to imagine or attempt to move his or her hand, the BCI translates that brain activity to a signal that triggers the FES. Our system adds an active component to the rehabilitation by linking brain activity to the peripheral stimulation device, which gives the patients direct control over their movement."
The Wisconsin team conducted a small clinical trial of their rehabilitation device, enlisting eight patients with one hand affected by stroke. The patients were also able to serve as a control group by using their normal, unaffected hand. Patients in the study represented a wide range of stroke severity and amount of time elapsed since the stroke occurred. Despite having received standard rehabilitative care, the patients had varying degrees of residual motor deficits in their upper extremities. Each underwent nine to 15 rehabilitation sessions of two to three hours with the new device over a period of three to six weeks.
The patients also underwent functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) before, at the mid-point of, at the end of, and one month following the rehabilitation period. fMRI is able to show which areas of the brain are activated while the patient performs a task, and DTI reveals the integrity of fibers within the white matter that connects the brain's functional areas.
Patients who suffered a stroke of moderate severity realized the greatest improvements to motor function following the rehabilitation sessions. Patients diagnosed with mild and severe strokes reported improved ability to complete activities of daily living following rehabilitation.
Dr. Prabhakaran said the results captured throughout the rehabilitation process—specifically the ratio of hemispheric involvement of motor areas—related well to the behavioral changes observed in patients. A comparison of pre-rehabilitation and post-rehabilitation fMRI results revealed reorganization in the regions of the brain responsible for motor function. DTI results over the course of the rehabilitation period revealed a gradual strengthening of the integrity of the fiber tracts.
"Our hope is that this device not only shortens rehabilitation time for stroke patients, but also that it brings a higher level of recovery than is achievable with the current standard of care," Dr. Prabhakaran said. "We believe brain imaging will be helpful in both planning and tracking a stroke patient's therapy, as well as learning more about neuroplastic changes during recovery."
Other co-authors are Dorothy Farrar-Edwards, Ph.D., Justin Sattin, M.D., Mitch Tyler, Ph.D., Veena A. Nair, Ph.D., Svyatoslav Vergun, B.S., Leo Walton, B.S., Jie Song, M.S., and Brittany Young, B.A., B.S.
# # #
Note: Copies of RSNA 2013 news releases and electronic images will be available online at RSNA.org/press13 beginning Monday, Dec. 2.
RSNA is an association of more than 53,000 radiologists, radiation oncologists, medical physicists and related scientists, promoting excellence in patient care and health care delivery through education, research and technologic innovation. The Society is based in Oak Brook, Ill. (RSNA.org)
Editor's note: The data in these releases may differ from those in the published abstract and those actually presented at the meeting, as researchers continue to update their data right up until the meeting. To ensure you are using the most up-to-date information, please call the RSNA Newsroom at 1-312-949-3233.
For patient-friendly information on stroke, visit RadiologyInfo.org.
| Abstract: |
Images (.JPG format)
 Figure 1. Brain activation patterns produced as patients tapped the fingers of their impaired hand before and after four to six weeks of therapy using the BCI-FES device. High-res (TIF) version (Right-click and Save As) |
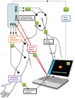 Figure 2. A schematic representation of the BCI-FES device indicating input and feedback components. High-res (TIF) version (Right-click and Save As) |
 Figure 3. A stroke patient receiving therapy using the BCI-FES device. High-res (TIF) version (Right-click and Save As) |

 PDF
PDF