RSNA Press Release
- Diffusion tensor imaging, an MRI technique, revealed signs of regional brain injury in patients with vestibulopathy after concussion.
- Patients with vestibular symptoms had white matter injury in the cerebellar area.
- Vestibulopathy was previously thought to be related to the inner ear structure.
MRI Pinpoints Region of Brain Injury in Some Concussion Patients
Released: April 15, 2014
| Media Contacts: | |
| RSNA Media Relations: | 1-630-590-7762 |
| Linda Brooks 1-630-590-7738 lbrooks@rsna.org |
Maureen Morley 1-630-590-7754 mmorley@rsna.org |
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Researchers using information provided by a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) technique have identified regional white matter damage in the brains of people who experience chronic dizziness and other symptoms after concussion.
The findings suggest that information provided by MRI can speed the onset of effective treatments for concussion patients. The results of this research are published online in the journal Radiology.
Concussions, also known as mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI), affect between 1.8 and 3.8 million individuals in the United States annually.
One of the most common and debilitating effects of concussion is vestibulopathy, a condition characterized by dizziness, imbalance and visual problems. Vestibulopathy impairs activities of daily living and puts patients at increased risk for a second injury. Up until now, no specific brain regions have been linked to the prognosis of patients with vestibulopathy.
For the study, the researchers retrospectively reviewed imaging data from 30 mTBI patients with vestibular symptoms and 25 with ocular convergence insufficiency, a condition that occurs when the eyes don't turn inward properly when focusing on a nearby object. Controls consisted of 39 mTBI patients without vestibular abnormalities and 17 with normal ocular convergence. The imaging data was acquired using an MRI technique called diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), which produces a fractional anisotropy (FA) value that can be used to determine damage to the brain's signal-transmitting white matter.
"FA provides a measure of how intact the white matter is," said Lea Alhilali, M.D., from the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center. "The lower the FA value, the more injured the white matter is."
When Dr. Alhilali and colleagues compared the DTI results, they found that the concussion patients with vestibular symptoms had decreased FA values in brain regions not previously suspected to be involved in post-traumatic vestibulopathy.
"Patients with vestibular symptoms had white matter injury in the cerebellar area, which is known to control balance and movement, and also in the fusiform gyri, a brain area that integrates the visual fields of the left and right eye and is important to spatial orientation," she said.
The findings appear to show a connection between vestibulopathy and regional brain damage, Dr. Alhilali added.
"Vestibulopathy was previously thought to be related to the inner ear structure," she said. "What's unique about our study is that it shows that, in these patients, there is also injury to the brain itself."
The researchers also found that injury to the cerebellar area was associated with a lengthier recovery time.
The findings have the potential to change the clinical management of vestibulopathy in concussion patients, Dr. Alhilali said. For example, DTI results could be used alongside neurocognitive testing to help determine a patient's prognosis and begin appropriate treatments.
"Vestibular therapy is often very effective," Dr. Alhilali said. "Using DTI findings, we can treat patients earlier and get them back to a baseline state much sooner."
The researchers have two goals in the near term, Dr. Alhilali said. First they want to identify brain injuries associated with other post-concussion symptoms, and then they hope to conduct prospective studies to track patients from shortly after their concussions through recovery.
"Concussion is not just one pathology, but many different injuries with different symptoms," Dr. Alhilali said. "Not every case is the same, and we need to treat each patient individually."
# # #
"Detection of Central White Matter Injury Underlying Vestibulopathy after Mild Traumatic Brain Injury." Collaborating with Dr. Alhilali were Karl Yaeger, M.D., Michael Collins, Ph.D., and Saeed Fakhran, M.D.
Radiology is edited by Herbert Y. Kressel, M.D., Harvard Medical School, Boston, Mass., and owned and published by the Radiological Society of North America, Inc. (http://radiology.rsna.org/)
RSNA is an association of more than 53,000 radiologists, radiation oncologists, medical physicists and related scientists, promoting excellence in patient care and health care delivery through education, research and technologic innovation. The Society is based in Oak Brook, Ill. (RSNA.org)
For patient-friendly information on MRI, visit RadiologyInfo.org.
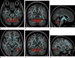 Figure 1. Vestibular disturbances correlate with decreased FA in cerebellar regions responsible for sensorimotor processing and central and/or axial balance as well as fusiform gyrus, which is responsible for visually guided locomotion and stereoscopic vision. Images derived from TBSS results and rendered on T1- weighted images from Montreal Neurologic Institute atlas indicate that significant white matter differences in patients with mild TBI and vestibular symptoms involve (a–c) lobule VI and vermian lobules VIIIa, VIIIb, and IX, as shown in axial (a), coronal (b), and sagittal (c) planes, and (d–f) fusiform gyri bilaterally, as shown in axial (d), coronal (e), and sagittal (f) planes. Significant voxels (P .05, corrected for multiple comparisons) were thickened by using TBSS fill function into local tracts (red) and overlaid on white matter skeleton (blue). High-res (TIF) version (Right-click and Save As) |
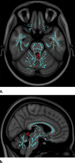 Figure 2. Vestibular disturbances correlate with increased mean diffusivity in vermian lobules of spinocerebellum, which processes proprioception input from spinal cord dorsal columns to anticipate future positioning during the course of a movement. Images derived from TBSS results and rendered on T1-weighted images from Montreal Neurologic Institute atlas indicate that significant white matter differences in patients with mild TBI and vestibular symptoms involve vermian lobules II and III, as shown in (a) axial and (b) sagittal planes. Significant voxels (P .05, corrected for multiple comparisons) were thickened by using TBSS fill function into local tracts (red) and overlaid on white matter skeleton (blue). High-res (TIF) version (Right-click and Save As) |
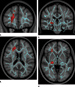 Figure 3. Convergence insufficiency correlates with increased FA in right anterior thalamic radiation, which is central to processing speed, and right geniculate nucleus optic radiations, the major relay station for the accommodation circuit central to oculomotor convergence. Asymmetric involvement of the right is not unexpected, as the corresponding left visual field is dominant for spatial processing as compared with the right visual field, which is dominant for nonspatial and/or temporal processing. Images derived from TBSS results and rendered on T1-weighted images from Montreal Neurologic Institute atlas show that significant white matter differences in patients with mild TBI and convergence insufficiency involve right anterior thalamic radiation, as shown in (a) coronal and (b) axial planes, and right geniculate nucleus optic radiations; as shown in (c) coronal and (d) axial planes. Significant voxels (P .05, corrected for multiple comparisons) were thickened by using TBSS fill function into local tracts (red) and overlaid on white matter skeleton (blue). High-res (TIF) version (Right-click and Save As) |

 PDF
PDF