Women with Coronary Artery Wall Thickness at Risk for Heart Disease
Released: April 25, 2019
At A Glance
- Researchers used CCTA and Framingham scores to assess coronary artery disease in 62 women and 62 men at low to intermediate risk of heart disease.
- Vessel wall thickness, as measured by MRI, was the strongest variable associated with coronary artery disease in women.
- The results point to a potential future role for vessel wall thickness measurements in identifying opportunities for early lifestyle changes or treatment.
- RSNA Media Relations
1-630-590-7762
media@rsna.org - Linda Brooks
1-630-590-7738
lbrooks@rsna.org - Dionna Arnold
1-630-590-7791
darnold@rsna.org
OAK BROOK, Ill. — The thickness of the coronary artery wall as measured by MRI is an independent marker for heart disease in women, according to a study published in the journal Radiology: Cardiothoracic Imaging.
Previous research has found limitations in cardiovascular risk assessment for women. For instance, there is evidence that the commonly used Framingham Risk Score, which provides estimates of cardiovascular disease risk based on age, sex and other factors, underestimates the chance of heart attacks and other cardiovascular events in asymptomatic women. Imaging tools like coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) tend to be used in patients with symptoms or more advanced cardiovascular disease, but are not recommended for liberal use in risk assessment among the general population with no cardiac symptoms.
Recently, cardiac MRI has emerged as a promising tool for early detection of coronary artery disease. MRI can detect thickening in the walls of the arteries, a change that occurs earlier in the course of heart disease than stenosis, or narrowing of the arteries.
"Despite the significant advances in CCTA technology, it is not appropriate to send all asymptomatic people to CCTA because of the exposure to radiation and chemical dyes used for imaging," said study lead author Khaled Z. Abd-Elmoniem, Ph.D., M.H.S., from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK), part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH) in Bethesda, Md. "MRI might be a safe alternative that can be used more broadly to assist in the diagnosis of coronary artery disease without exposing patients to a procedure that carries some risk. The advantage of MRI in this situation is that it can tell us that there is a thickening before stenosis, which is difficult to do with CCTA."
Over a period of years, Dr. Abd-Elmoniem and colleagues developed and refined an MRI technique that adjusts for the motions of breathing and the beating heart to directly visualize coronary wall thickness. They used the technique to assess coronary artery disease in 62 women and 62 men with low to intermediate risks based on their Framingham scores. The patients also underwent CCTA to investigate the association between vessel wall thickness and CCTA-based coronary artery disease scores.
The results showed stark differences between the two groups.
"When we separated the patients into men and women, coronary artery disease in men was, as expected, associated with aging and a high Framingham score," said Dr. Abd-Elmoniem. "However, in women, both age and the Framingham score were not factors. Vessel wall thickness, as measured by MRI, was the strongest variable associated with coronary artery disease."
The results point to a potential future role for vessel wall thickness measurements in identifying opportunities for early lifestyle changes or treatment in a young, asymptomatic population. Unlike CCTA, cardiac MRI does not require radiation or contrast dyes.
"A single image and measurement of coronary vessel wall thickness with MRI can be used to gauge the extent of coronary plaque in asymptomatic women, who then can be appropriately referred for further exams and/or treatment," said Dr. Abd-Elmoniem.
While further studies are needed, these results emphasize the unique nature of coronary artery disease development in women compared to men, and show that MRI could one day be a useful tool in the prevention and management of the disease in women, especially for those with intermediate risk.
"MRI provides another way to help guide physicians toward therapy," said NIDDK's Ahmed M. Gharib, M.D., a co-author on the paper. "Since it can be repeated, it can also be useful in monitoring the effectiveness of any therapy."
Dr. Gharib, who heads the NIDDK Biomedical and Metabolic Imaging Branch, said the study results represent the fruits of a collaboration across multiple disciplines.
"This is a wonderful example of how a multidisciplinary team of biomedical engineers and radiologists can expedite translational research to clinical radiological applications," he said.
"Sexual Dimorphism of Coronary Artery Disease in a Low- and Intermediate-Risk Asymptomatic Population: Association with Coronary Vessel Wall Thickness at MRI in Women." Collaborating with Drs. Abd-Elmoniem and Gharib were Ahmed M. Ghanem, Ph.D., Jatin Raj Matta, Dr.Ph., P.A.-C, Reham Elgarf, Ahmed Hamimi, M.D., Ranganath Muniyappa, M.D., Hadjira Ishaq, B.S., Colleen Hadigan, M.D., and Michael V. McConnell, M.D., M.S.E.E.
Radiology: Cardiothoracic Imaging is edited by Suhny Abbara, M.D., University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, and owned and published by the Radiological Society of North America, Inc. (https://pubs.rsna.org/cardiothoracic-imaging)
RSNA is an association of over 53,400 radiologists, radiation oncologists, medical physicists and related scientists, promoting excellence in patient care and health care delivery through education, research and technologic innovation. The Society is based in Oak Brook, Ill. (RSNA.org)
For patient-friendly information on MRI and CCTA, visit RadiologyInfo.org.
Images (.JPG and .TIF format)
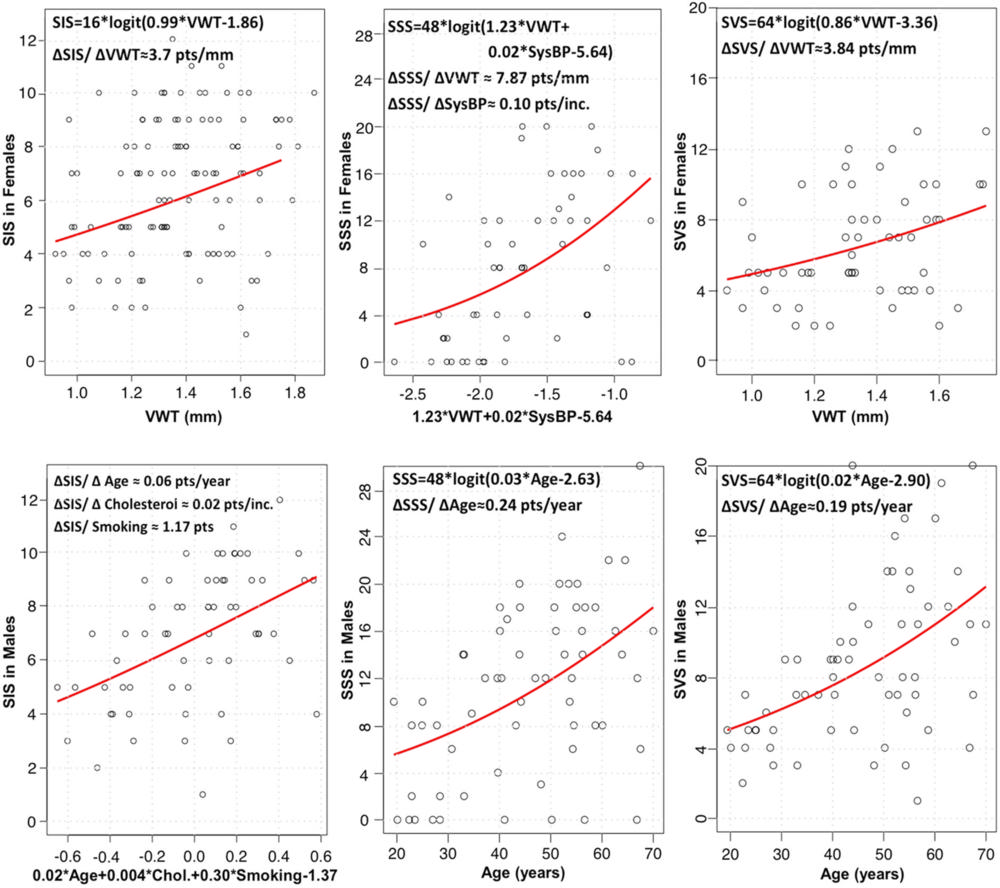
Figure 1. Binomial-logit regression models and the local marginal associations between statistically significant factors and normalized coronary artery disease scores for segment involvement score (SIS), segment stenosis score (SSS), and segment volume score (SVS) in women and men. Coronary vessel wall thickness (VWT) was the strongest surrogate of coronary artery disease scores in women, whereas age was the strongest risk factor in men. ∆ = change in, Chol = cholesterol, pts = points, SysBP = systolic blood pressure.
High-res (TIF) version
(Right-click and Save As)
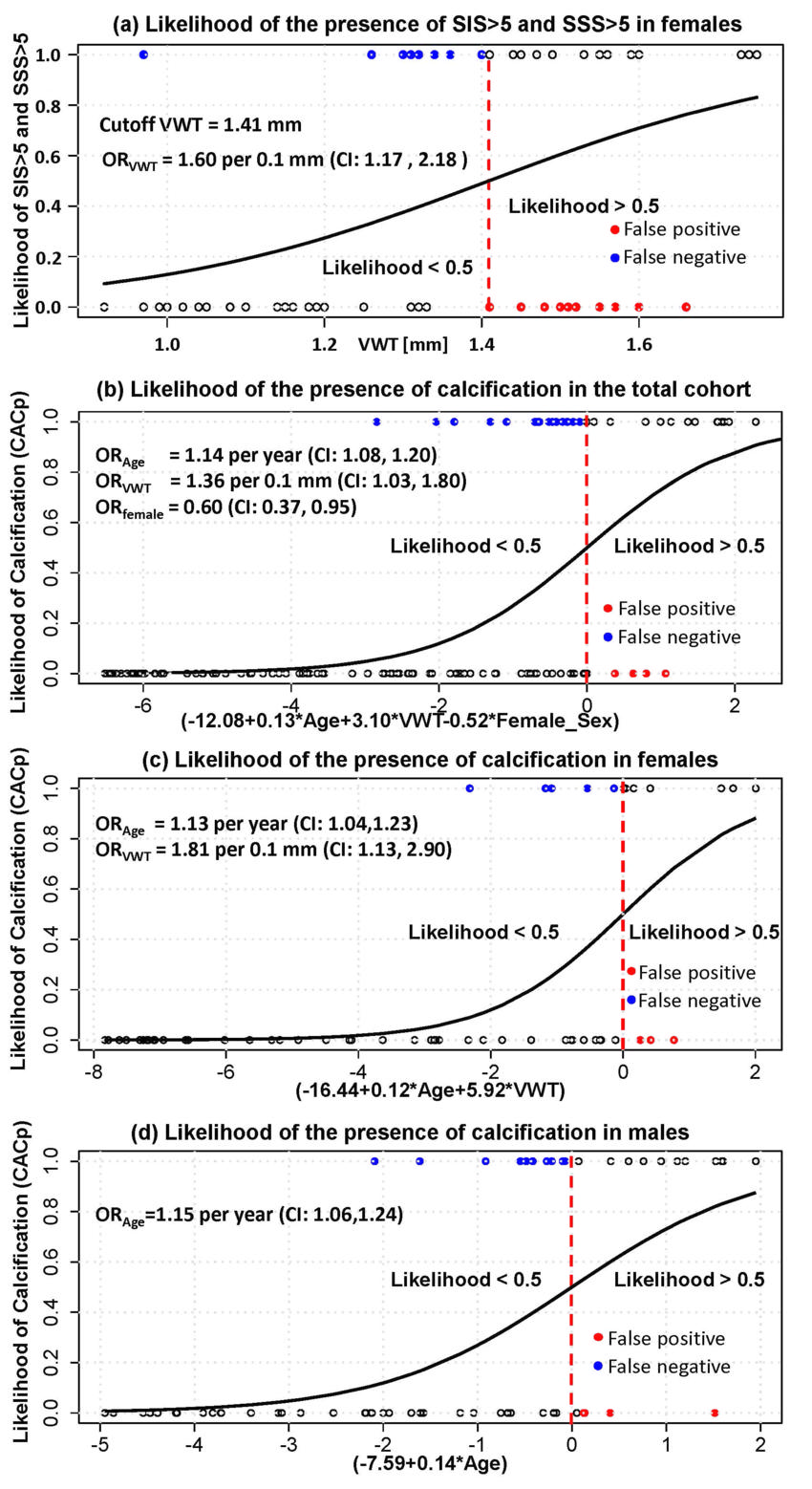
Figure 2. Likelihood probability curves showing the likelihood of having (a) coronary segment involvement score (SIS) and coronary segment stenosis score (SSS) greater than 5 in women in relation to coronary vessel wall thickness (VWT) and (b) calcified plaque in the total cohort, (c) in women, and (d) in men as a function of statistically significant factors. CI = confidence interval, OR = odds ratio, ORage = odds ratio of age, ORfemale = odds ratio of women, ORVWT = odds ratio of VWT.
High-res (TIF) version
(Right-click and Save As)

Figure 3. Coronary vessel wall CT angiographic images (multiplanar reformatted stretch view). Images in a 46-year-old asymptomatic woman show, A, measured vessel wall thickness of 1.3 mm (black arrows) and, B, noncalcified plaque (white arrow) in the proximal left anterior descending coronary artery. Coronary CT angiographic images in the left anterior descending artery in a 44-year-old asymptomatic woman show, C, thicker coronary vessel wall (black arrows) and, D, coronary artery disease (white arrows).
High-res (TIF) version
(Right-click and Save As)

